十
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Han character
[edit]十 (Kangxi radical 24, 十+0, 2 strokes, cangjie input 十 (J), four-corner 40000, composition ⿻一丨)
- Kangxi radical #24, ⼗.
- Shuowen Jiezi radical №54
Derived characters
[edit]- Appendix:Chinese radical/十
- 什, 𰃵, 廾, 叶, 𡈿, 㚈, 𢌗, 汁, 䦹, 辻, 旪, 𬁰, 瓧, 𤽁, 𭾗, 𥎧, 竍, 籵, 𥾅, 𨒒, 計(计), 𧾽, 兙, 針(针), 𮪦, 𨔿, 𫙏, 𪗕, 𭃄, 𨙩, 𩡪
- 干, 仐, 𠓝, 𠤏, 𠫘, 夲, 𫵱, 𢨦, 早, 毕, 氒, 𦉲, 𠅋, 𤬧, 𤯀, 皁, 𥃪, 𮂯, 辛, 𦉴, 䘚, 阜, 𥤿, 隼, 𢈰, 章, 率, 𠵀, 䭴, 準(凖), 𤔭, 𮍞
- 土, 士, 支, 古, 𪞱, 𥃭, 孛, 壴, 直, 真, 索, 𩖘, 𢛳, 㥁, 疐, 伞, 傘, 𣎳, 畞, 賫(赍), 賷, 䥅, 𭻹, 戎, 𢦏, 𬺱, 𣂑, 𭂩, 𫭂
References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 155, character 17
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 2695
- Dae Jaweon: page 348, character 6
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 58, character 9
- Unihan data for U+5341
Chinese
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
十 | |
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | 拾 financial 什 | |
Glyph origin
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 十 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Spring and Autumn | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | |||
| Bronze inscriptions | Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|

|

|

|

|

|
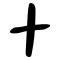
|

|

|
Unlike 一, which was one horizontal stroke meaning one, 十 was originally simply a vertical stroke. In later forms 一 was added, forming a cross.
Possibly a pictogram (象形) for a needle, later written as 針 (OC *kjum, *kjums), borrowed phonetically for 十 (OC *ɡjub, “ten”).
Unrelated to 支, 卖, 直, 真, 德, 甫, and 七 but related to the original version of 丈 and perhaps related to 由.
Etymology
[edit]From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *gip.
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard)
- (Chengdu, Sichuanese Pinyin): si2
- (Xi'an, Guanzhong Pinyin): shí
- (Nanjing, Nanjing Pinyin): shii̊q
- (Dungan, Cyrillic and Wiktionary): шы (šɨ, I)
- Cantonese
- (Guangzhou–Hong Kong, Jyutping): sap6
- (Dongguan, Jyutping++): sok8
- (Taishan, Wiktionary): sip5
- (Yangjiang, Jyutping++): sap6
- (Guangzhou–Hong Kong, Jyutping): sap6
- Gan (Wiktionary): siit7
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): seh5
- Northern Min (KCR): sí / sī
- Eastern Min (BUC): sĕk
- Puxian Min (Pouseng Ping'ing): sae2 / sieh7 / seh7 / sih7
- Southern Min
- Wu (Northern, Wugniu): 8zeq / 1so / 3so / 5so / 7seq
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): shr6
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄕˊ
- Tongyong Pinyin: shíh
- Wade–Giles: shih2
- Yale: shŕ
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: shyr
- Palladius: ши (ši)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʂʐ̩³⁵/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: si2
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: s
- Sinological IPA (key): /sz̩²¹/
- (Xi'an)
- Guanzhong Pinyin: shí
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʂʐ̩²⁴/
- (Nanjing)
- Nanjing Pinyin: shii̊q
- Nanjing Pinyin (numbered): shiiq5
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʂʐ̩ʔ⁵/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: шы (šɨ, I)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʂʐ̩²⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: sap6
- Yale: sahp
- Cantonese Pinyin: sap9
- Guangdong Romanization: seb6
- Sinological IPA (key): /sɐp̚²/
- (Dongguan, Guancheng)
- Jyutping++: sok8
- Sinological IPA (key): /sɔk̚²²/
- (Taishanese, Taicheng)
- Wiktionary: sip5
- Sinological IPA (key): /sip̚³²/
- (Yangjiang Yue, Jiangcheng)
- Jyutping++: sap6
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʃɐp̚⁵⁵/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: siit7
- Sinological IPA (key): /sɨt̚²/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: sṳ̍p
- Hakka Romanization System: siib
- Hagfa Pinyim: sib6
- Sinological IPA: /sɨp̚⁵/
- (Hailu, incl. Zhudong)
- Hakka Romanization System: shibˋ
- Sinological IPA: /ʃip²/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: seh5
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /səʔ⁵⁴/
- (Taiyuan)+
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: sí / sī
- Sinological IPA (key): /si⁵⁴/, /si⁵⁵/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: sĕk
- Sinological IPA (key): /sɛiʔ⁵/
- (Fuzhou)
- Puxian Min
- (Putian)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: sae2
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɬɛ¹³/
- (Xianyou)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: sieh7
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɬiɛʔ²⁴/
- (Putian)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: seh7
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɬɛʔ⁴/
- (Xianyou)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: seh7
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɬɛʔ²⁴/
- (Putian)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: sih7
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɬiʔ⁴/
- (Xianyou)
- Pouseng Ping'ing: sih7
- Sinological IPA (key): /ɬiʔ²⁴/
- (Putian)
- Southern Min
- cha̍p - vernacular;
- si̍p/se̍p - literary.
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: zab8 / zag8
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: tsa̍p / tsa̍k
- Sinological IPA (key): /t͡sap̚⁴/, /t͡sak̚⁴/
- zab8 - Chaozhou, Shantou, Jieyang, Chaoyang, Raoping, Pontianak;
- zag8 - Chenghai.
- Dialectal data
- Middle Chinese: dzyip
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*t.[ɡ]əp/
- (Zhengzhang): /*ɡjub/
Definitions
[edit]十
See also
[edit]| Chinese numbers | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 106 | 108 | 1012 | |
| Normal (小寫 / 小写) |
〇, 零, 空 | 一, 蜀 | 二, 兩 / 两 | 三 | 四 | 五 | 六 | 七 | 八 | 九 | 十 | 百 | 千 | 萬 / 万, 十千 (Malaysia, Singapore) |
百萬 / 百万, 桶(Philippines), 面桶 (Philippines) |
億 / 亿 | 兆 (Taiwan) 萬億 / 万亿 (Mainland China) |
| Financial (大寫 / 大写) |
零 | 壹 | 貳 / 贰 | 參 / 叁 | 肆 | 伍 | 陸 / 陆 | 柒 | 捌 | 玖 | 拾 | 佰 | 仟 | ||||
Compounds
[edit]- 一五一十 (yīwǔyīshí)
- 一以當十 / 一以当十
- 一暴十寒 (yīpùshíhán)
- 一曝十寒 (yīpù-shíhán)
- 一漿十餅 / 一浆十饼 (yījiāngshíbǐng)
- 一目十行 (yīmùshíháng)
- 一饋十起 / 一馈十起
- 七十二 (qīshí'èr)
- 七十二候 (Qīshí'èrhòu)
- 七十二墳 / 七十二坟
- 七十二子 (qīshí'èr zǐ)
- 七十二帝
- 七十二沽
- 七十二營 / 七十二营
- 七十二行
- 七十二變 / 七十二变
- 七十二賢 / 七十二贤
- 七十二鑽 / 七十二钻
- 七十子 (qīshízǐ)
- 七十瓦上霜,八十不稀奇 (qīshí wǎ shàng shuāng, bāshí bù xīqí)
- 七十說 / 七十说
- 七十鑽 / 七十钻
- 七十鳥 / 七十鸟
- 丁娘十索
- 七方十齊 / 七方十齐
- 七老八十 (qīlǎobāshí)
- 三十 (sānshí)
- 三十三天
- 三十二天
- 三十二相
- 三十六 (sānshíliù)
- 三十六國 / 三十六国
- 三十六天
- 三十六宮 / 三十六宫
- 三十六峰
- 三十六書 / 三十六书
- 三十六物
- 三十六界
- 三十六策
- 三十六苑
- 三十六行
- 三十六計 / 三十六计 (Sānshíliù Jì)
- 三十六郡
- 三十六陂
- 三十六雨
- 三十六體 / 三十六体
- 三十六鱗 / 三十六鳞
- 三十哥
- 三十子
- 三十晚上
- 三十有室
- 三十而立 (sānshí'érlì)
- 三島十洲 / 三岛十洲
- 三賢十聖 / 三贤十圣
- 三風十愆 / 三风十愆
- 不十分
- 么花十八
- 九儒十丐
- 九十 (jiǔshí)
- 九故十親 / 九故十亲
- 九流十家
- 九變十化 / 九变十化
- 二十 (èrshí)
- 二十一史
- 二十一條 / 二十一条
- 二十一經 / 二十一经
- 二十二史
- 二十五史
- 二十五弦
- 二十五絃 / 二十五弦
- 二十五老
- 二十八天
- 二十八宿 (Èrshíbā Xiù)
- 二十八將 / 二十八将
- 二十八星
- 二十八次
- 二十八舍
- 二十八調 / 二十八调
- 二十六史
- 二十四 (èrshísì)
- 二十四友
- 二十四司
- 二十四史 (Èrshísì Shǐ)
- 二十四品
- 二十四孝 (Èrshísì Xiào)
- 二十四旗
- 二十四時 / 二十四时
- 二十四橋 / 二十四桥
- 二十四氣 / 二十四气
- 二十四治
- 二十四神
- 二十四節 / 二十四节
- 二十四韻 / 二十四韵
- 五代十國 / 五代十国 (Wǔdài Shíguó)
- 五光十色 (wǔguāngshísè)
- 五十 (wǔshí)
- 五十三參 / 五十三参
- 五十弦
- 五十肩 (wǔshíjiān)
- 五風十雨 / 五风十雨 (wǔfēngshíyǔ)
- 京都十景
- 以一擊十 / 以一击十
- 以一當十 / 以一当十
- 信心十足
- 八九不離十 / 八九不离十 (bā jiǔ bù lí shí)
- 八十 (bāshí)
- 八十一章
- 八十二好
- 八十億劫 / 八十亿劫
- 八十四調 / 八十四调
- 八十壋 / 八十垱 (Bāshídàng)
- 八十孩兒 / 八十孩儿
- 八十種好 / 八十种好
- 八文十二
- 八棒十挾 / 八棒十挟
- 八棒十枷
- 六十 (liùshí)
- 六十四卦
- 六十甲子 (liùshí jiǎzǐ)
- 六十種曲 / 六十种曲
- 六十調 / 六十调
- 初一十五 (chūyī shíwǔ)
- 勁道十足 / 劲道十足
- 北十 (Běishí)
- 北郭十友
- 十一 (shíyī)
- 十一千百
- 十一年
- 十一月 (shíyīyuè)
- 十一月份 (Shíyīyuèfèn)
- 十一而稅 / 十一而税
- 十一號 / 十一号
- 十一路
- 十七 (shíqī)
- 十七八
- 十七史
- 十七孔橋 / 十七孔桥
- 十七字詩 / 十七字诗
- 十七帖
- 十七弟子
- 十三 (shísān)
- 十上
- 十三史
- 十三太保 (shísān tàibǎo)
- 十三家
- 十三弦
- 十三日
- 十三月
- 十三樓 / 十三楼
- 十三省
- 十三科
- 十三篇
- 十三經 / 十三经 (Shísānjīng)
- 十三行 (Shísānháng)
- 十三調 / 十三调
- 十三轍 / 十三辙
- 十三間樓 / 十三间楼
- 十三陵 (Shísānlíng)
- 十三點 / 十三点 (shísāndiǎn)
- 十不
- 十不當一 / 十不当一
- 十不閑 / 十不闲 (shíbùxián)
- 十世單傳 / 十世单传
- 十世宥
- 十世宥能
- 十中八九
- 十之八九 (shízhībājiǔ)
- 十九 (shíjiǔ)
- 十九人
- 十九信條 / 十九信条
- 十九路
- 十九路軍 / 十九路军
- 十亂 / 十乱
- 十事
- 十二 (shí'èr)
- 十二使徒
- 十二入
- 十二公
- 十二分 (shí'èrfēn)
- 十二分之一
- 十二分教
- 十二分星
- 十二分野
- 十二博士
- 十二卿
- 十二和
- 十二哲
- 十二因緣 / 十二因缘
- 十二國 / 十二国
- 十二地支
- 十二女
- 十二子
- 十二客
- 十二宮 / 十二宫 (shí'èrgōng)
- 十二層 / 十二层
- 十二屬 / 十二属
- 十二峰
- 十二巫峰
- 十二平均律 (shí'èr píngjūnlǜ)
- 十二度
- 十二律 (shí'èrlǜ)
- 十二戟
- 十二指腸 / 十二指肠 (shí'èrzhǐcháng)
- 十二指陽 / 十二指阳
- 十二支 (shí'èrzhī)
- 十二旒
- 十二星座 (shí'èr xīngzuò)
- 十二時 / 十二时
- 十二時慢 / 十二时慢
- 十二時盤 / 十二时盘
- 十二時神 / 十二时神
- 十二時蟲 / 十二时虫
- 十二時辰 / 十二时辰
- 十二晚峰
- 十二月 (shí'èryuè)
- 十二月份 (Shí'èryuèfèn)
- 十二月律
- 十二枝
- 十二樓 / 十二楼
- 十二次 (shí'èrcì)
- 十二牧
- 十二物
- 十二獸 / 十二兽
- 十二生肖 (shí'èr shēngxiào)
- 十二監 / 十二监
- 十二相屬 / 十二相属
- 十二碧峰
- 十二碼 / 十二码 (shí'èrmǎ)
- 十二碼球 / 十二码球
- 十二神
- 十二萬分 / 十二万分
- 十二筒
- 十二紅 / 十二红
- 十二經 / 十二经
- 十二經脈 / 十二经脉
- 十二緣起 / 十二缘起
- 十二肖
- 十二肢
- 十二脈 / 十二脉
- 十二舍
- 十二處 / 十二处
- 十二蟲 / 十二虫
- 十二街
- 十二衢
- 十二衣
- 十二角形
- 十二調 / 十二调
- 十二諸侯 / 十二诸侯
- 十二象
- 十二辰
- 十二辰堆
- 十二辰屬 / 十二辰属
- 十二辰神
- 十二辰蟲 / 十二辰虫
- 十二進法 / 十二进法
- 十二道
- 十二邊形 / 十二边形
- 十二重樓 / 十二重楼
- 十二金人
- 十二金牌
- 十二金釵 / 十二金钗
- 十二鍾 / 十二钟
- 十二鐘 / 十二钟
- 十二門 / 十二门
- 十二門論 / 十二门论
- 十二闌干
- 十二面體 / 十二面体
- 十二章
- 十二食
- 十五 (shíwǔ)
- 十五年
- 十五時 / 十五时
- 十人饌 / 十人馔
- 十代冥王
- 十位 (shíwèi)
- 十住
- 十伯
- 十使
- 十保扶
- 十倍
- 十倫 / 十伦
- 十停
- 十億 / 十亿 (shíyì)
- 十億位元 / 十亿位元
- 十億位元以太網絡 / 十亿位元以太网络
- 十光五色
- 十克
- 十全 (shíquán)
- 十全十美 (shíquánshíměi)
- 十全大補湯 / 十全大补汤 (shí quán dà bǔ tāng)
- 十全老人
- 十八 (shíbā)
- 十八世
- 十八九
- 十八事
- 十八侯
- 十八公
- 十八地獄 / 十八地狱
- 十八姨
- 十八娘
- 十八子
- 十八子兒 / 十八子儿
- 十八學士 / 十八学士
- 十八房
- 十八灘 / 十八滩
- 十八獄 / 十八狱
- 十八界
- 十八省
- 十八相送
- 十八羅漢 / 十八罗汉 (Shíbā Luóhàn)
- 十八般
- 十八變 / 十八变
- 十八賢 / 十八贤
- 十八路
- 十八高賢 / 十八高贤
- 十六 (shíliù)
- 十六位元
- 十六國 / 十六国 (Shíliù-Guó)
- 十六天魔
- 十六字令
- 十六字訣 / 十六字诀
- 十六宅
- 十六才子
- 十六族
- 十六樓 / 十六楼
- 十六烷值
- 十六相
- 十六羅漢 / 十六罗汉
- 十六衛 / 十六卫
- 十六角
- 十六進制 / 十六进制
- 十六院
- 十冬臘月 / 十冬腊月 (shídōnglàyuè)
- 十分 (shífēn)
- 十分之一
- 十剎海 / 十刹海
- 十劑 / 十剂
- 十力
- 十勢 / 十势
- 十十五五
- 十千 (shíqiān)
- 十升
- 十半
- 十反
- 十友
- 十口相傳 / 十口相传
- 十史
- 十吋口炮
- 十吏札
- 十命
- 十哲
- 十善
- 十善道
- 十四 (shísì)
- 十四弦
- 十四樓 / 十四楼
- 十四絃 / 十四弦
- 十四經 / 十四经
- 十四行詩 / 十四行诗 (shísìhángshī)
- 十因
- 十國 / 十国 (Shíguó)
- 十國春秋 / 十国春秋
- 十圍 / 十围
- 十圍五攻 / 十围五攻
- 十地
- 十堯 / 十尧
- 十堰 (Shíyàn)
- 十堰市
- 十多億 / 十多亿
- 十大家
- 十大建設 / 十大建设
- 十大弟子
- 十大曲
- 十大洞天
- 十夫
- 十夫客
- 十天干
- 十夫楺椎
- 十夫橈椎 / 十夫桡椎
- 十失
- 十如是
- 十姊妹 (shízǐmèi)
- 十姓百名
- 十姓部落
- 十子
- 十字 (shízì)
- 十字口
- 十字坡
- 十字庫 / 十字库
- 十字形
- 十字架 (shízìjià)
- 十字架刑
- 十字格
- 十字溝 / 十字沟 (Shízìgōu)
- 十字繡 / 十字绣 (shízìxiù)
- 十字花押
- 十字花科 (shízìhuākē)
- 十字街 (shízìjiē)
- 十字街口 (shízì jiēkǒu)
- 十字街頭 / 十字街头
- 十字路 (shízìlù)
- 十字路口 (shízìlùkǒu)
- 十字路頭 / 十字路头
- 十字軍 / 十字军 (shízìjūn)
- 十字鎬 / 十字镐 (shízìgǎo)
- 十字頭螺刀 / 十字头螺刀
- 十字餅 / 十字饼
- 十守
- 十宗
- 十室
- 十客
- 十室九匱 / 十室九匮
- 十室九空 (shíshìjiǔkōng)
- 十室容賢 / 十室容贤
- 十家
- 十家連坐 / 十家连坐
- 十家香
- 十寒一暴
- 十尖
- 十居其九
- 十嶺 / 十岭 (Shílǐng)
- 十州
- 十巴拄 (si̍p-pa-tú) (Min Nan)
- 十布
- 十帝
- 十常侍 (shíchángshì)
- 十干 (shígān)
- 十年 (shínián)
- 十年九澇 / 十年九涝
- 十年九潦
- 十年九荒
- 十年內亂 / 十年内乱
- 十年動亂 / 十年动乱 (shínián dòngluàn)
- 十年寒窗
- 十年書 / 十年书
- 十年樹木,百年樹人 / 十年树木,百年树人 (shínián shùmù, bǎinián shùrén)
- 十年河東,十年河西 / 十年河东,十年河西 (shí nián hé dōng, shí nián hé xī)
- 十年浩劫 (shínián hàojié)
- 十年磨劍 / 十年磨剑
- 十年窗下
- 十年讀書 / 十年读书
- 十幹 / 十干
- 十幾 / 十几 (shíjǐ)
- 十幾個月 / 十几个月
- 十德
- 十思
- 十惡 / 十恶 (shí'è)
- 十惡不赦 / 十恶不赦 (shí'èbùshè)
- 十惡五逆 / 十恶五逆
- 十意
- 十愆
- 十成
- 十成九穩 / 十成九稳
- 十戒 (shíjiè)
- 十戰十勝 / 十战十胜
- 十才子
- 十手爭指 / 十手争指
- 十拗
- 十抽一
- 十拏九穩 / 十拿九稳
- 十指
- 十拷九棒
- 十拿九穩 / 十拿九稳 (shínájiǔwěn)
- 十指倉 / 十指仓
- 十指連心 / 十指连心
- 十指露縫 / 十指露缝
- 十捉九著
- 十教
- 十敗 / 十败
- 十數 / 十数
- 十方 (shífāng)
- 十方世界
- 十方地面
- 十方常住
- 十方界
- 十族
- 十日 (shírì)
- 十日並出 / 十日并出
- 十日平原
- 十日歡 / 十日欢
- 十日談 / 十日谈 (Shírì Tán)
- 十日飲 / 十日饮
- 十旬
- 十時 / 十时
- 十景櫥 / 十景橱
- 十月 (shíyuè)
- 十月之交
- 十月份 (Shíyuèfèn)
- 十月懷胎 / 十月怀胎 (shíyuèhuáitāi)
- 十月朝
- 十月桃
- 十月革命 (Shíyuè Gémìng)
- 十有八九 (shíyǒubājiǔ)
- 十朋
- 十朋之龜 / 十朋之龟
- 十望
- 十榦 / 十干
- 十樣景 / 十样景
- 十樣蠻牋 / 十样蛮笺
- 十樣錦 / 十样锦
- 十款
- 十款天條 / 十款天条
- 十死
- 十死一生
- 十死不問 / 十死不问
- 十死九活
- 十死九生
- 十殿
- 十殿閻王 / 十殿阎王
- 十母
- 十洲
- 十洲三島 / 十洲三岛
- 十洋錦 / 十洋锦
- 十清九濁 / 十清九浊
- 十漿 / 十浆
- 十漿五饋 / 十浆五馈
- 十滴水
- 十煇 / 十辉
- 十玄
- 十玄門 / 十玄门
- 十率
- 十王
- 十王宅
- 十王殿
- 十生九死
- 十界
- 十畝之間 / 十亩之间
- 十番 (shífān)
- 十番鼓 (shífāngǔ)
- 十病九痛
- 十發十中 / 十发十中
- 十目一行
- 十目十手
- 十目所視 / 十目所视
- 十直
- 十直日
- 十眉
- 十相俱足
- 十相具足
- 十眉圖 / 十眉图
- 十眠九坐
- 十萬 / 十万 (shíwàn)
- 十萬位 / 十万位
- 十萬八千里 (shí wàn bā qiān lǐ)
- 十萬火急 / 十万火急 (shíwànhuǒjí)
- 十萬火速 / 十万火速
- 十科
- 十箭
- 十米九糠
- 十紀 / 十纪
- 十經 / 十经
- 十經童子 / 十经童子
- 十緊 / 十紧
- 十總布 / 十总布
- 十羊九牧
- 十美圖 / 十美图
- 十義 / 十义
- 十翼
- 十色
- 十蕩十決 / 十荡十决
- 十藪 / 十薮
- 十號 / 十号
- 十行
- 十行俱下
- 十行本
- 十行詔 / 十行诏
- 十裂
- 十襲 / 十袭
- 十親九故 / 十亲九故
- 十親九眷 / 十亲九眷
- 十角
- 十角形 (shíjiǎoxíng)
- 十言
- 十言之教
- 十設 / 十设
- 十誡 / 十诫 (shíjiè)
- 十變五化 / 十变五化
- 十賚 / 十赉
- 十賭九輸 / 十赌九输 (shídǔjiǔshū)
- 十足 (shízú)
- 十載寒窗 / 十载寒窗
- 十輩 / 十辈
- 十轉九空 / 十转九空
- 十返
- 十連 / 十连
- 十通
- 十進 / 十进 (shíjìn)
- 十進位 / 十进位 (shíjìnwèi)
- 十進位法 / 十进位法
- 十進分類法 / 十进分类法 (shíjìn fēnlèifǎ)
- 十進制 / 十进制 (shíjìnzhì)
- 十進法 / 十进法
- 十進算術 / 十进算术
- 十過 / 十过
- 十道
- 十邊形 / 十边形
- 十郎八當 / 十郎八当
- 十部
- 十部從事 / 十部从事
- 十部樂 / 十部乐
- 十酒
- 十里 (Shílǐ)
- 十里堡 (Shílǐpù)
- 十里洋場 (shílǐyángchǎng)
- 十里紅樓 / 十里红楼
- 十里鋪 (Shílǐpù)
- 十里長亭
- 十里鼻
- 十重
- 十金
- 十錦 / 十锦 (shíjǐn)
- 十錢主簿 / 十钱主簿
- 十鑽 / 十钻
- 十門 / 十门
- 十阿父
- 十際 / 十际
- 十離詩 / 十离诗
- 十雨五風 / 十雨五风
- 十面埋伏 (shímiànmáifú)
- 十韋 / 十韦
- 十項 / 十项
- 十項全能 / 十项全能 (shíxiàng quánnéng)
- 十項運動 / 十项运动
- 十頭 / 十头
- 十頭添撇 / 十头添撇
- 十風五雨 / 十风五雨
- 十駕 / 十驾
- 十驥 / 十骥
- 十體 / 十体
- 十體書 / 十体书
- 十魔
- 十鼠同穴
- 十鼠爭穴 / 十鼠争穴
- 十齋 / 十斋
- 十齋日 / 十斋日
- 十齋期 / 十斋期
- 吃一看十
- 合十 (héshí)
- 吃十方
- 問一答十 / 问一答十
- 問十道百 / 问十道百
- 四十 (sìshí)
- 大年三十 (dànián sānshí)
- 封十八姨
- 布被十年
- 常十萬 / 常十万
- 平原十日
- 年三十 (niánsānshí)
- 得一望十
- 憋十
- 打十三
- 拔十失五
- 拔十得五
- 指一說十 / 指一说十
- 撮十
- 攢十字 / 攒十字
- 斃十 / 毙十
- 方外十友
- 李十二
- 杜十姨
- 杜十娘
- 李十郎
- 梏十指
- 橫羅十字 / 横罗十字
- 歸十歸一 / 归十归一
- 沒十成 / 没十成
- 用一當十 / 用一当十
- 畫十字 / 画十字
- 當十錢 / 当十钱
- 百兒八十 / 百儿八十 (bǎi'erbāshí)
- 百十 (bǎishí)
- 目下十行
- 福無十全 / 福无十全
- 粗十番
- 粗細十番 / 粗细十番
- 紅十字會 / 红十字会 (Hóngshízìhuì)
- 素十番
- 素十錦 / 素十锦
- 細十番 / 细十番
- 羿斃十日 / 羿毙十日
- 耕十畝田 / 耕十亩田
- 聞一知十 / 闻一知十 (wényīzhīshí)
- 聲價十倍 / 声价十倍
- 聲譽十倍 / 声誉十倍
- 肏你祖宗十八代 (cào nǐ zǔzōng shíbā dài)
- 舉十知九 / 举十知九
- 花十八
- 菩薩十地 / 菩萨十地
- 藍十字會 / 蓝十字会
- 西十 (Xīshí)
- 西泠十子
- 言十妄九
- 赤十字會 / 赤十字会
- 足了十人
- 運十 / 运十
- 重十
- 金釵十二 / 金钗十二
- 鈷六十 / 钴六十
- 鐵十字 / 铁十字
- 長十八 / 长十八
- 閉十 / 闭十
- 閩中十子 / 闽中十子
- 雙十 / 双十
- 雙十節 / 双十节 (Shuāngshíjié)
- 音學十書 / 音学十书
- 飛天十響 / 飞天十响
- 飢餓三十 / 饥饿三十
- 駑馬十舍 / 驽马十舍
- 駑馬十駕 / 驽马十驾
- 驕氣十足 / 骄气十足
- 鬥十胡 / 斗十胡
Descendants
[edit]Others:
- → Ahom: 𑜏𑜢𑜆𑜫 (sip)
- → Bouyei: xib
- → Khmer: ដប់ (dɑp), សិប (səp)
- → Lao: ສິບ (sip)
- → Lü: ᦉᦲᧇ (ṡiib)
- → Saek: ซิ̄บ
- → Shan: သိပ်း (síp)
- → Tai Dam: ꪎꪲꪚ
- → Tai Nüa: ᥔᥤᥙᥴ (síp)
- → Thai: สิบ (sìp)
- → Zhuang: cib
Japanese
[edit]| < 9 | 10 | 11 > |
|---|---|---|
| Cardinal : 十 | ||
Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]- Go-on: じゅう (jū, Jōyō)←じふ (zifu, historical)
- Kan-on: しゅう (shū)←しふ (sifu, historical)
- Kan’yō-on: じっ (ji', Jōyō)、じゅっ (ju')
- Kun: と (to, 十, Jōyō)、とお (tō, 十, Jōyō)←とを (towo, 十, historical)、そ (so, 十)
- Nanori: い (i)、か (ka)、かず (kazu)、ぎ (gi)、さ (sa)、し (shi)、しげ (shige)、そう (sō)、ただ (tada)、ち (chi)、とみ (tomi)、ね (ne)、ひさし (hisashi)、ま (ma)、みつ (mitsu)、みつる (mitsuru)、る (ru)、わ (wa)
Compounds
[edit]Etymology 1
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 十 |
| じゅう Grade: 1 |
| goon |
| Alternative spelling |
|---|
| 拾 (financial) |
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 十 |
| じっ Grade: 1 |
| kan'yōon |
/ʑipʉ/ → /ʑiɸu/ → /ʑɨu/ → /ʑuː//ʑiʔ/ → /ʑi~̚/
From Middle Chinese 十 (MC dzyip).
Pronunciation
[edit]Numeral
[edit]Derived terms
[edit]Idioms
[edit]- 一から十まで (ichi kara jū made)
Proverbs
[edit]- 一を聞いて十を知る (ichi o kiite jū o shiru)
Noun
[edit]Affix
[edit]十 or 十 • (jū- or ji'-) ←じふ (zifu)?
Derived terms
[edit]- 十雨 (jūu)
- 十戒, 十誡 (jikkai)
- 十月 (jūgatsu)
- 十干 (jikkan)
- 十指 (jisshi)
- 十字 (jūji)
- 十姉妹 (jūshimatsu)
- 十中八九 (jitchūhakku), 十中八九 (jūchūhakku)
- 十手 (jitte)
- 十種競技 (jisshukyōgi, “decathlon”)
- 十進法 (jisshinhō, “decimal system”)
- 十全 (jūzen)
- 十哲 (jittetsu)
- 十人 (jūnin)
- 十年 (jūnen)
- 十念 (jūnen)
- 十能 (jūnō, “small fire shovel”)
- 十把一絡げ (jippa hitokarage)
- 十分 (jūbun)
- 十万億土 (jūman'okudo)
- 十目 (jūmoku)
- 十薬 (jūyaku)
Etymology 2
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 十 |
| とお Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
⟨to2wo⟩ → */təwo/ → /towo/ → /toː/
From Old Japanese, ultimately from Proto-Japonic *təwə.
Pronunciation
[edit]Numeral
[edit]Derived terms
[edit]Idioms
[edit]Proverbs
[edit]- 十で神童十五で才子二十過ぎればただの人 (tō de shindō jūgo de saishi hatachi sugireba tada no hito)
Etymology 3
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 十 |
| と Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
Shift from tō above.[2]
Pronunciation
[edit]Numeral
[edit]Derived terms
[edit]Etymology 4
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 十 |
| そ Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
⟨so1⟩ → */sʷo/ → /so/
From Old Japanese.
Used in compounds.
Affix
[edit]- multiplied by ten: tenfold
Derived terms
[edit]Etymology 5
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 十 |
| しい Grade: 1 |
| irregular |
Numeral
[edit]Derived terms
[edit]Coordinate terms
[edit]References
[edit]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ^ “十”, in 日本国語大辞典 [Nihon Kokugo Daijiten][1] (in Japanese), concise edition, Tokyo: Shogakukan, 2006
- ^ “十”, in デジタル大辞泉 [Digital Daijisen][2] (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, updated roughly every four months
Korean
[edit]| 100 | ||||
| ← 1 | ← 9 | 10 | 11 → | 20 → |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||
| Native isol.: 열 (yeol) Native attr.: 열 (yeol) Sino-Korean: 십 (sip) Hanja: 十 Ordinal: 열째 (yeoljjae) | ||||
Etymology
[edit]From Middle Chinese 十 (MC dzyip).
| Historical Readings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dongguk Jeongun Reading | ||
| Dongguk Jeongun, 1448 | 씹〮 (Yale: ssíp) | |
| Middle Korean | ||
| Text | Eumhun | |
| Gloss (hun) | Reading | |
| Hunmong Jahoe, 1527[3] | 열〮 (Yale: yél) | 십〮 (Yale: síp) |
Pronunciation
[edit]- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [ɕʰip̚]
- Phonetic hangul: [십]
Hanja
[edit]Compounds
[edit]- 십간 (十干, sipgan)
- 십계 (十戒, sipgye)
- 십구 (十九, sipgu)
- 십만 (十萬, simman)
- 십분 (十分, sipbun)
- 십사 (十四, sipsa)
- 십삼 (十三, sipsam)
- 십억 (十億, sibeok)
- 십오 (十五, sibo)
- 십육 (十六, sibyuk)
- 십이 (十二, sibi)
- 십일 (十一, sibil)
- 십자 (十字, sipja)
- 십전 (十全, sipjeon)
- 십칠 (十七, sipchil)
- 십팔 (十八, sip'pal)
- 시월 (十月, siwol)
- 구십 (九十, gusip)
- 사십 (四十, sasip)
- 삼십 (三十, samsip)
- 수십 (數十, susip)
- 오십 (五十, osip)
- 육십 (六十, yuksip)
- 이십 (二十, isip)
- 칠십 (七十, chilsip)
- 팔십 (八十, palsip)
- 십계명 (十誡命, sipgyemyeong)
- 십이월 (十二月, sibiwol)
- 십이지 (十二支, sibiji)
- 십일월 (十一月, sibirwol)
- 십일조 (十一租, sibiljo)
- 십자가 (十字架, sipjaga)
- 십자군 (十字軍, sipjagun)
- 십자선 (十字線, sipjaseon)
- 십자성 (十字星, sipjaseong)
- 십장생 (十長生, sipjangsaeng)
- 십진법 (十進法, sipjinbeop)
- 쌍십절 (雙十節, ssangsipjeol)
- 적십자 (赤十字, jeoksipja)
- 십이지장 (十二指腸, sibijijang)
- 십중팔구 (十中八九, sipjungpalgu)
References
[edit]- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [4]
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]十: Hán Việt readings: thập (
十: Nôm readings: thập[1][2][4]
Derived terms
[edit]- 紅十字 (Hồng Thập Tự)
- 五代十國 (Ngũ Đại Thập Quốc)
- 率十 (suất thập)
- 三十六計 (Tam thập lục kế)
- 十惡 (thập ác)
- 十道 (thập đạo)
- 十紀 (thập kỉ, “decade”)
- 十六分 (thập lục phân)
- 十年 (thập niên, “decade”)
- 十分 (thập phân, “decimal”)
- 十方 (thập phương, “everywhere”)
- 十成 (thập thành)
- 十字 (thập tự, “cross, 十-shaped”)
- 十死一生 (thập tử nhất sinh)
References
[edit]- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Enclosed CJK Letters and Months block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Shuowen radicals
- Han pictograms
- Chinese terms inherited from Proto-Sino-Tibetan
- Chinese terms derived from Proto-Sino-Tibetan
- Mandarin terms with audio pronunciation
- Cantonese terms with audio pronunciation
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Puxian Min lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Sichuanese hanzi
- Dungan hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Taishanese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Puxian Min hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese numerals
- Mandarin numerals
- Sichuanese numerals
- Dungan numerals
- Cantonese numerals
- Taishanese numerals
- Gan numerals
- Hakka numerals
- Jin numerals
- Northern Min numerals
- Eastern Min numerals
- Hokkien numerals
- Teochew numerals
- Puxian Min numerals
- Wu numerals
- Xiang numerals
- Middle Chinese numerals
- Old Chinese numerals
- Chinese adjectives
- Mandarin adjectives
- Sichuanese adjectives
- Dungan adjectives
- Cantonese adjectives
- Taishanese adjectives
- Gan adjectives
- Hakka adjectives
- Jin adjectives
- Northern Min adjectives
- Eastern Min adjectives
- Hokkien adjectives
- Teochew adjectives
- Puxian Min adjectives
- Wu adjectives
- Xiang adjectives
- Middle Chinese adjectives
- Old Chinese adjectives
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 十
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese cardinal numbers
- Beginning Mandarin
- Chinese numeral symbols
- zh:Ten
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese first grade kanji
- Japanese kyōiku kanji
- Japanese jōyō kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading じゅう
- Japanese kanji with historical goon reading じふ
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading しゅう
- Japanese kanji with historical kan'on reading しふ
- Japanese kanji with kan'yōon reading じっ
- Japanese kanji with kan'yōon reading じゅっ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading と
- Japanese kanji with kun reading とお
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading とを
- Japanese kanji with kun reading そ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading い
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading か
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading かず
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ぎ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading さ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading し
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading しげ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading そう
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ただ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ち
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading とみ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ね
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ひさし
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ま
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading みつ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading みつる
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading る
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading わ
- Japanese terms spelled with 十 read as じゅう
- Japanese terms read with goon
- Japanese terms spelled with 十 read as じっ
- Japanese terms read with kan'yōon
- Japanese terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese terms with audio pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese numerals
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Japanese terms with 1 kanji
- Japanese terms spelled with 十
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese affixes
- Japanese terms spelled with 十 read as とお
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms inherited from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms derived from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms historically spelled with を
- Japanese terms spelled with 十 read as と
- Japanese terms spelled with 十 read as そ
- Japanese terms read with irregular kanji readings
- Japanese terms borrowed from Mandarin
- Japanese terms derived from Mandarin
- ja:Numbers
- Japanese numeral symbols
- ja:Ten
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Korean numeral symbols
- ko:Ten
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Nom
- Vietnamese numeral symbols
- CJKV radicals



