代
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Han character
[edit]代 (Kangxi radical 9, 人+3, 5 strokes, cangjie input 人戈心 (OIP), four-corner 23240, composition ⿰亻弋)
Derived characters
[edit]References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 93, character 11
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 386
- Dae Jaweon: page 197, character 7
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 113, character 5
- Unihan data for U+4EE3
Chinese
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
代 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 代 | |
|---|---|
| Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
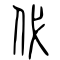
|
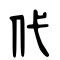
|
|
References:
Mostly from Richard Sears' Chinese Etymology site (authorisation),
| |
| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 戴 | *ʔl'ɯːɡs |
| 襶 | *tɯːɡs |
| 貸 | *l̥ʰɯːɡs |
| 代 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 袋 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 岱 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 黛 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 玳 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 帒 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 甙 | *l'ɯːɡs |
| 酨 | *l'ɯːs, *zlɯːs |
| 試 | *hljɯɡs |
| 弒 | *hljɯɡs |
| 忒 | *l̥ʰɯːɡ |
| 貣 | *l̥ʰɯːɡ, *l'ɯːɡ |
| 鴏 | *l'ɯːɡ |
| 栻 | *l̥ʰɯɡ, *hljɯɡ |
| 侙 | *l̥ʰɯɡ |
| 恜 | *l̥ʰɯɡ |
| 式 | *hljɯɡ |
| 軾 | *hljɯɡ |
| 拭 | *hljɯɡ |
| 鉽 | *hljɯɡ |
| 烒 | *hljɯɡ |
| 弋 | *lɯɡ |
| 芅 | *lɯɡ |
| 黓 | *lɯɡ |
| 隿 | *lɯɡ |
| 杙 | *lɯɡ |
| 釴 | *lɯɡ |
Phono-semantic compound (形聲 / 形声, OC *l'ɯːɡs): semantic 亻 (“person”) + phonetic 弋 (OC *lɯɡ)
Etymology 1
[edit]- state's name → toponym
| This etymology is missing or incomplete. Please add to it, or discuss it at the Etymology scriptorium. Particularly: “Is 代 (OC *lˤək-s) related to 狄 (OC *lˤek, “northern barbarians”), the Spring and Autumn state's founders?” |
Most of the people with this surname in Mainland China were originally with the surname 戴 (Dài) and was a result of second-round simplification of Chinese characters.
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard)
- (Chengdu, Sichuanese Pinyin): dai4
- (Dungan, Cyrillic and Wiktionary): дэ (de, III)
- Cantonese
- Gan (Wiktionary): tai5
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): dai3
- Northern Min (KCR): dō
- Eastern Min (BUC): dô̤i / dâi
- Southern Min
- Wu (Northern, Wugniu): 6de
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): tai5 / tai4
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄉㄞˋ
- Tongyong Pinyin: dài
- Wade–Giles: tai4
- Yale: dài
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: day
- Palladius: дай (daj)
- Sinological IPA (key): /taɪ̯⁵¹/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: dai4
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: dai
- Sinological IPA (key): /tai²¹³/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: дэ (de, III)
- Sinological IPA (key): /tɛ⁴⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: doi6
- Yale: doih
- Cantonese Pinyin: doi6
- Guangdong Romanization: doi6
- Sinological IPA (key): /tɔːi̯²²/
- (Taishanese, Taicheng)
- Wiktionary: oi5
- Sinological IPA (key): /ᵘɔi³²/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: tai5
- Sinological IPA (key): /tʰai¹¹/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: thoi / tai
- Hakka Romanization System: toi / dai
- Hagfa Pinyim: toi4 / dai4
- Sinological IPA: /tʰoi̯⁵⁵/, /tai̯⁵⁵/
- (Meixian)
- (Hailu, incl. Zhudong)
- Hakka Romanization System: toi˖ / daiˇ
- Sinological IPA: /tʰoi³³/, /tai¹¹/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: dai3
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /tai⁴⁵/
- (Taiyuan)+
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: dō
- Sinological IPA (key): /to⁵⁵/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: dô̤i / dâi
- Sinological IPA (key): /tɔy²⁴²/, /tɑi²⁴²/
- (Fuzhou)
- dô̤i - vernacular;
- dâi - literary.
- Southern Min
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Zhangzhou, General Taiwanese)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: tē
- Tâi-lô: tē
- Phofsit Daibuun: de
- IPA (Xiamen, Zhangzhou): /te²²/
- IPA (Taipei, Kaohsiung): /te³³/
- (Hokkien: Quanzhou)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: tēr
- Tâi-lô: tēr
- IPA (Quanzhou): /tə⁴¹/
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Quanzhou, Zhangzhou, General Taiwanese)
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Quanzhou, Zhangzhou, General Taiwanese)
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Zhangzhou, General Taiwanese)
- tē/tēr - vernacular;
- tāi - literary;
- tài - literary (limited, e.g. 交代).
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: do7 / dai3 / toi3 / toih4
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: tō / tài / thòi / thoih
- Sinological IPA (key): /to¹¹/, /tai²¹³/, /tʰoi²¹³/, /tʰoiʔ²/
- do7 - vernacular ("generation / dynasty / period");
- dai3 - literary (in 交代);
- toi3 - semantic ("to act for/as").
- tai5 - literary;
- tai4 - colloquial.
- Dialectal data
- Middle Chinese: dojH
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*lˤək-s/
- (Zhengzhang): /*l'ɯːɡs/
Definitions
[edit]代
- to replace; to take the place of
- to act for; to do something on behalf of
- to act as; to be the acting (president etc.)
- generation; age group
- historical period; era
- date; age
- dynasty; line of rulers
- (geology) era (geochronologic unit)
- (grammar) Short for 代名詞/代名词 (dàimíngcí); short for 代詞/代词 (dàicí, “pronoun”).
- (historical geography) Short for 代國/代国 (Dàiguó, “state of Dai”).
- a surname
Synonyms
[edit]- (generation): 世 (shì)
Compounds
[edit]- 一代 (yīdài)
- 一代兒 / 一代儿
- 一代宗匠
- 一代宗臣
- 一代巨擘
- 一代文宗
- 一代楷模
- 一代談宗 / 一代谈宗
- 一代風流 / 一代风流
- 一代鼎臣
- 一生一代
- 七代先靈 / 七代先灵
- 七窩八代 / 七窝八代
- 上代 (shàngdài)
- 三代 (sāndài)
- 三代人物
- 三代同堂
- 三代執金 / 三代执金
- 世世代代 (shìshìdàidài)
- 世代 (shìdài)
- 世代交替
- 中代
- 中生代
- 九代
- 亂代 / 乱代
- 二代 (èrdài)
- 五代 (Wǔdài)
- 互代
- 五代十國 / 五代十国 (Wǔdài Shíguó)
- 五代史
- 亙代 / 亘代
- 交代 (jiāodài)
- 人事代謝 / 人事代谢
- 人代
- 人民代表 (rénmín dàibiǎo)
- 今代
- 代下
- 代乳粉
- 代人
- 代人受過 / 代人受过
- 代人捉刀
- 代付 (dàifù)
- 代代 (dàidài)
- 代代相傳 / 代代相传 (dàidàixiāngchuán)
- 代代花 (dàidàihuā)
- 代作 (dàizuò)
- 代位
- 代位權 / 代位权
- 代位繼承 / 代位继承
- 代倩
- 以倭代唐
- 以倭代華 / 以倭代华
- 代價 / 代价 (dàijià)
- 代償 / 代偿 (dàicháng)
- 代力
- 代勞 / 代劳
- 代北
- 代匠
- 代匱 / 代匮
- 代及
- 代史
- 代名詞 / 代名词 (dàimíngcí)
- 代哭
- 代唱
- 代售 (dàishòu)
- 代國 / 代国 (Dàiguó)
- 代培 (dàipéi)
- 代執行 / 代执行
- 代墊 / 代垫
- 代天巡狩
- 代奏
- 代姓
- 代嬗
- 代字
- 代宗
- 代官
- 代室
- 代寫 / 代写 (dàixiě)
- 代州 (Dàizhōu)
- 代工 (dàigōng)
- 以工代賑 / 以工代赈 (yǐgōng daìzhèn)
- 代序 (dàixù)
- 代庖 (dàipáo)
- 代庸
- 代德
- 代手
- 代打 (dàidǎ)
- 代拜
- 代拆代行
- 代指 (dàizhǐ)
- 代換 / 代换 (dàihuàn)
- 代收 (dàishōu)
- 代敘 / 代叙
- 代數 / 代数 (dàishù)
- 代數學 / 代数学 (dàishùxué)
- 代數式 / 代数式 (dàishùshì)
- 代斲
- 代明
- 代易
- 代書 / 代书 (dàishū)
- 代替 (dàitì)
- 代替品
- 代替物
- 代替財 / 代替财
- 代本
- 代杖
- 代東 / 代东
- 代板
- 以桃代李
- 代步 (dàibù)
- 代母 (dàimǔ)
- 代比
- 代淨 / 代净
- 代溝 / 代沟 (dàigōu)
- 代漏龍 / 代漏龙
- 代濟 / 代济
- 代為 / 代为 (dàiwéi)
- 代為說項 / 代为说项
- 代父 (dàifù)
- 代班
- 代理 (dàilǐ)
- 代理人 (dàilǐrén)
- 代理商 (dàilǐshāng)
- 代理戰爭 / 代理战争
- 代用 (dàiyòng)
- 代用品 (dàiyòngpǐn)
- 代田
- 代田法
- 代留
- 代碼 / 代码 (dàimǎ)
- 代碼機 / 代码机
- 代稱 / 代称 (dàichēng)
- 代立
- 代筆 / 代笔 (dàibǐ)
- 代筆遺囑 / 代笔遗嘱
- 代管 (dàiguǎn)
- 代籍
- 代糖 (dàitáng)
- 代紀 / 代纪
- 代終 / 代终
- 代縣 / 代县 (Dàixiàn)
- 代罪羔羊 (dàizuì gāoyáng)
- 代翟
- 代耕
- 以耳代目
- 代脈 / 代脉
- 代興 / 代兴
- 代舍
- 代舞
- 代英
- 代茶
- 以茶代酒 (yǐchádàijiǔ)
- 代號 / 代号 (dàihào)
- 以蠟代薪 / 以蜡代薪
- 代行 (dàixíng)
- 代表 (dàibiǎo)
- 代表作 (dàibiǎozuò)
- 代表團 / 代表团 (dàibiǎotuán)
- 代襲 / 代袭
- 代見 / 代见
- 代解
- 代言 (dàiyán)
- 代言人 (dàiyánrén)
- 以計代戰 / 以计代战
- 代詞 / 代词 (dàicí)
- 代語 / 代语
- 代課 / 代课 (dàikè)
- 代謝 / 代谢 (dàixiè)
- 代謝作用 / 代谢作用
- 代議制 / 代议制 (dàiyìzhì)
- 代議士 / 代议士 (dàiyìshì)
- 代議政治 / 代议政治
- 代谷
- 代購 / 代购 (dàigòu)
- 代贖 / 代赎 (dàishú)
- 代起
- 代越
- 代越庖俎
- 代身
- 代輸 / 代输
- 代辦 / 代办 (dàibàn)
- 代追
- 代運 / 代运
- 代遷 / 代迁
- 代邀
- 代還 / 代还
- 代邸
- 代郡 (Dàijùn)
- 代郵 / 代邮
- 代金 (dàijīn)
- 代銷 / 代销 (dàixiāo)
- 代銷商 / 代销商
- 代雁
- 代電 / 代电
- 代面
- 以韓代明 / 以韩代明
- 代領 / 代领 (dàilǐng)
- 代食
- 代飯 / 代饭
- 代馬 / 代马
- 代馬依風 / 代马依风
- 代馬望北 / 代马望北
- 休代
- 來代 / 来代
- 倩代
- 借代 (jièdài)
- 傳代 / 传代 (chuándài)
- 傳宗接代 / 传宗接代 (chuánzōngjiēdài)
- 僑選代表 / 侨选代表
- 億代 / 亿代
- 僵李代桃
- 僵桃代李
- 元生代
- 先代 (xiāndài)
- 全權代表 / 全权代表
- 八代 (Bādài)
- 六代
- 公侯萬代 / 公侯万代
- 共同代理
- 共同代表
- 共和時代 / 共和时代
- 冠代
- 冰河時代 / 冰河时代
- 列代
- 前五代
- 前代 (qiándài)
- 劃時代 / 划时代 (huàshídài)
- 勝代 / 胜代
- 包辦代替 / 包办代替 (bāobàn dàitì)
- 十代冥王
- 千秋萬代 / 千秋万代 (qiānqiūwàndài)
- 千齡萬代 / 千龄万代
- 升級換代 / 升级换代
- 即代
- 原子時代 / 原子时代
- 原生代 (Yuánshēngdài)
- 厭代 / 厌代
- 及瓜而代
- 叔代
- 受代
- 取代 (qǔdài)
- 取而代之 (qǔ'érdàizhī)
- 古代 (gǔdài)
- 史前時代 / 史前时代 (shǐqián shídài)
- 古生代 (Gǔshēng Dài)
- 吉格代加依 (Jígédàijiāyī)
- 告代
- 君權時代 / 君权时代
- 命代
- 四代
- 國代 / 国代
- 國大代表 / 国大代表
- 地代
- 基礎代謝 / 基础代谢 (jīchǔ dàixiè)
- 增額國代 / 增额国代
- 多歷年代 / 多历年代
- 太古代 (Tàigǔdài)
- 天工人代
- 奕代
- 嬗代
- 子代
- 季代
- 孢子世代
- 將李代桃 / 将李代桃
- 尸祝代庖
- 布代
- 布林代數 / 布林代数
- 希代
- 幕府時代 / 幕府时代
- 年代 (niándài)
- 年湮代遠 / 年湮代远
- 庖代
- 彌代 / 弥代
- 往代
- 後五代 / 后五代
- 後代 / 后代 (hòudài)
- 得代
- 恆代遺風 / 恒代遗风
- 恐怖時代 / 恐怖时代
- 懸壺代哭 / 悬壶代哭
- 成年古代
- 戰代 / 战代
- 戰國時代 / 战国时代 (Zhànguó Shídài)
- 指代 (zhǐdài)
- 换代 (huàndài)
- 換代 / 换代 (huàndài)
- 搖籃時代 / 摇篮时代
- 擔代 / 担代
- 攘代
- 攝代 / 摄代
- 改姓易代
- 改朝換代 / 改朝换代 (gǎicháohuàndài)
- 啟蒙時代 / 启蒙时代 (Qǐméng Shídài)
- 新五代史
- 新故代謝 / 新故代谢
- 新時代 / 新时代 (xīnshídài)
- 新生代
- 新陳代謝 / 新陈代谢 (xīnchén dàixiè)
- 斷代 / 断代 (duàndài)
- 斷代史 / 断代史 (duàndàishǐ)
- 日據時代 / 日据时代
- 日治時代 / 日治时代
- 易代
- 明代 (Míngdài)
- 昭代
- 時代 / 时代 (shídài)
- 時代病 / 时代病
- 時代精神 / 时代精神 (shídài jīngshén)
- 時代週刊 / 时代周刊
- 晚代
- 曠代 / 旷代
- 曠代一人 / 旷代一人
- 曩代
- 更代 (gēngdài)
- 更新換代 / 更新换代
- 替代 (tìdài)
- 替代作用
- 替代品 (tìdàipǐn)
- 替代能源
- 朝代 (cháodài)
- 末代 (mòdài)
- 末代孫 / 末代孙
- 末代皇帝
- 李代桃僵 (lǐdàitáojiāng)
- 李代桃殭 / 李代桃僵
- 桃僵李代
- 棄代 / 弃代
- 橋代 / 桥代
- 權代 / 权代
- 歲代 / 岁代
- 歷代 / 历代 (lìdài)
- 歷史時代 / 历史时代
- 殊代
- 民代 (míndài)
- 民意代表 (mínyì dàibiǎo)
- 永代
- 求代
- 沒代 / 没代
- 注代
- 法定代理
- 洪荒時代 / 洪荒时代
- 海權時代 / 海权时代
- 清代 (Qīngdài)
- 漁獵時代 / 渔猎时代
- 濁代 / 浊代
- 激素替代療法 / 激素替代疗法 (jīsù tìdài liáofǎ)
- 濟代 / 济代
- 燕代 (Yān Dài)
- 燕雁代飛 / 燕雁代飞
- 猒代
- 班代
- 班代表
- 理代
- 現代 / 现代 (xiàndài)
- 現代主義 / 现代主义 (xiàndài zhǔyì)
- 現代人 / 现代人 (xiàndàirén)
- 現代化 / 现代化 (xiàndàihuà)
- 現代史 / 现代史
- 現代建築 / 现代建筑
- 現代戲 / 现代戏
- 現代繪畫 / 现代绘画
- 現代舞 / 现代舞 (xiàndàiwǔ)
- 現代芭蕾 / 现代芭蕾
- 現代藝術 / 现代艺术
- 現代詩 / 现代诗
- 理性時代 / 理性时代
- 瓜代 (guādài)
- 生代
- 用代楮敬
- 異代 / 异代
- 番代
- 當代 / 当代 (dāngdài)
- 疇代 / 畴代
- 疑問代詞 / 疑问代词 (yíwèn dàicí)
- 百代
- 百代城
- 百代文宗
- 百代過客 / 百代过客
- 皇代
- 盛代
- 石器時代 / 石器时代 (Shíqì Shídài)
- 祖代 (zǔdài)
- 祖宗三代 (zǔzōng sān dài)
- 祖宗八代
- 神權時代 / 神权时代
- 禪代 / 禅代
- 萬代 / 万代 (wàndài)
- 萬代一時 / 万代一时
- 萬代千秋 / 万代千秋 (wàndàiqiānqiū)
- 秦二代
- 稀代
- 積代 / 积代
- 空間時代 / 空间时代
- 第二代
- 篡代
- 簡代 / 简代
- 累代 (lěidài)
- 絕代 / 绝代 (juédài)
- 絕代佳人 / 绝代佳人
- 綿代 / 绵代
- 線性代數 / 线性代数 (xiànxìng dàishù)
- 緩步代車 / 缓步代车
- 總代理 / 总代理
- 纂代
- 繼代 / 继代
- 聖代 / 圣代 (shèngdài)
- 肏你祖宗十八代 (cào nǐ zǔzōng shíbā dài)
- 胞子世代
- 臨時代辦 / 临时代办
- 興代 / 兴代
- 舊五代史 / 旧五代史
- 蓋代 / 盖代
- 藉箸代籌 / 借箸代筹
- 補代 / 补代
- 親代 / 亲代
- 討替代 / 讨替代
- 請代 / 请代
- 談判代表 / 谈判代表
- 資代 / 资代
- 資訊時代 / 资讯时代
- 越俎代庖 (yuèzǔdàipáo)
- 越俎代謀 / 越俎代谋
- 輒代 / 辄代
- 輓代 / 挽代
- 近代 (jìndài)
- 迭代 (diédài)
- 違代 / 违代
- 遐代
- 運代 / 运代
- 遞代 / 递代
- 遠代 / 远代
- 遠古時代 / 远古时代
- 遷代 / 迁代
- 遺臭萬代 / 遗臭万代
- 邏輯代數 / 逻辑代数
- 配子世代
- 重代
- 銅器時代 / 铜器时代
- 鐵器時代 / 铁器时代 (Tiěqì Shídài)
- 閒代 / 闲代
- 隔代 (gédài)
- 隔代遺傳 / 隔代遗传 (gédài yíchuán)
- 霸代日
- 青銅時代 / 青铜时代 (qīngtóng shídài)
- 革代
- 頃代 / 顷代
- 頂代 / 顶代
- 頂名代告 / 顶名代告
- 風華絕代 / 风华绝代
- 香煙後代 / 香烟后代
- 驕代 / 骄代
- 驚代 / 惊代
- 黃金時代 / 黄金时代 (huángjīn shídài)
- 黑暗時代 / 黑暗时代 (Hēi'ànshídài)
- 黨代表 / 党代表 (dǎngdàibiǎo)
Descendants
[edit]Others:
Etymology 2
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]- Southern Min (Hokkien, POJ): tāi
Definitions
[edit]代
Compounds
[edit]Etymology 3
[edit]| For pronunciation and definitions of 代 – see 戴 (“to wear something on the head; to carry on the head; etc.”). (This character is the second-round simplified form of 戴). |
Notes:
|
References
[edit]- “代”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[1], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]- Go-on: だい (dai, Jōyō)
- Kan-on: たい (tai, Jōyō)
- Kun: かわる (kawaru, 代わる, Jōyō)、かわる (kawaru, 代る)、かわり (kawari, 代り)、かわり (kawari, 代わり)、かえる (kaeru, 代える, Jōyō)、よ (yo, 代, Jōyō)、しろ (shiro, 代, Jōyō)
- Nanori: す (su)
Compounds
[edit]- 代わる, 代る (kawaru, “succeed, relieve”)
- 代わり, 代り (kawari, “substitute, replacement”)
- 代わり, 代り (-gawari, “substitute for”)
- 代える (kaeru, “replace, exchange”)
- 代え (kae, “change, alteration”)
- 代代, 代々 (daidai), 代代, 代々 (yoyo, “for generations”)
- 代案 (daian, “alternate plan”)
- 代位 (daī, “subrogation, substitution”)
- 代印 (daīn, “signing by proxy”)
- 代員 (daīn, “proxy”)
- 代演 (daien, “substitute for another”)
- 代価 (daika, “price, cost”)
- 代官 (daikan, “Edo-period prefectural governor”)
- 代艦 (daikan, “replacement warship”)
- 代願 (daigan, “praying by proxy”)
- 代議 (daigi, “representing others in a conference”)
- 代休 (daikyū, “compensatory holiday”)
- 代金 (daikin, “price, payment”)
- 代言 (daigen, “advocacy”)
- 代行 (daikō, “acting as agent”)
- 代講 (daikō, “substitute lecturing”)
- 代作 (daisaku, “ghost-writing”)
- 代参 (daisan, “visiting a temple for another”)
- 代謝 (daisha, “renewal, regeneration”)
- 代車 (daisha, “loaner vehicle”)
- 代署 (daisho, “sign for another”)
- 代書 (daisho, “amanuensis, scribe”)
- 代償 (daishō, “compensation, indemnification”)
- 代将 (daishō, “brigadier general”)
- 代親 (daishin, “godparent”)
- 代診 (daishin, “doctor's assistance”)
- 代数 (daisū, “algebra”)
- 代僧 (daisō, “substitute priest”)
- 代走 (daisō, “substitute runner”)
- 代打 (daida, “pinch-hitting”)
- 代替 (daitai), 代替 (daigae, “substitution, alternation”)
- 代地 (daichi, “substitute land”)
- 代置 (daichi, “replace”)
- 代読 (daidoku, “reading for another”)
- 代入 (dainyū, “substitution, assignment”)
- 代人 (dainin, “substitute, deputy”)
- 代任 (dainin, “agency, acting official”)
- 代納 (dainō, “payment for another”)
- 代筆 (daihitsu, “amanuensis”)
- 代表 (daihyō, “representative, representation”)
- 代品 (daihin, “substitute article”)
- 代父 (daifu, “godfather”)
- 代物 (daibutsu, “substitute”)
- 代返 (daihen, “answer a roll call for another”)
- 代弁 (daiben, “pay by proxy”)
- 代母 (daibo, “godmother”)
- 代務 (daimu, “vicarious management”)
- 代役 (daiyaku, “substitute, substitution”)
- 代用 (daiyō, “substitution”)
- 代理 (dairi, “representation, agency”)
- 代赭 (taisha, “red ocher”)
- 代物 (shiromono, “thing, article”)
- 代掻き, 代き (shirokaki, “preparing a rice field for planting”)
- 代引き (daibiki, “cash on delivery”)
- 代待ち (daimachi, “waiting in place of someone else”)
- 代替え (daigae, “substitution, alternation”)
- 代稽古 (daigeiko, “substitute teaching”)
- 代執行 (daishikkō, “carrying out by proxy”)
- 代神楽 (daikagura, “grand kagura performance”)
- 代諾者 (daidakusha, “legal representative”)
- 代当主 (daitōshu, “nth-generation head of a family”)
- 代動詞 (daidōshi, “pro-verb”)
- 代燃車 (dainensha, “car running on substitute fuel”)
- 代名詞 (daimeishi, “pronoun”)
- 代理人 (dairinin, “representative, deputy”)
- 代議士 (daigishi, “member of the Diet”)
- 代替エネルギー (daitai enerugī, “alternative energy”)
- 代名動詞 (daimei-dōshi, “pronominal verb”)
- 代が変わる (dai ga kawaru, “change hands”)
- 揚代, 揚げ代 (agedai, “fee paid for a geisha”)
- 足代 (ashidai, “traveling expenses”)
- 阿代 (ashiro, “Ophidion asiro”)
- 網代 (ajiro, “wickerwork”)
- 網代 (amishiro, “dividing up a fishing catch”)
- 幾代 (ikuyo, “generations, ages”)
- 一代 (ichidai, “generation, lifetime”)
- 永代 (eitai, “permanence, eternity”)
- 往代 (ōdai, “ancient times”)
- 形代 (katashiro, “representation of a sacred object”)
- 壁代 (kabeshiro, “separating curtain”)
- 神代 (kamiyo), 神代 (jindai, “ancient time”)
- 関代 (kandai, “relative pronoun”)
- 希代, 稀代 (kidai), 希代, 稀代 (kitai, “rarity, uncommonness”)
- 近代 (kindai, “present day”)
- 玉代 (gyokudai, “time charge for a geisha”)
- 薬代 (kusuridai, “charge for medicine”)
- 車代 (kurumadai, “carfare, cartage fee”)
- 現代 (gendai, “nowadays, modern era”)
- 更代 (kōtai, “exchange”)
- 後代 (kōdai, “posterity”)
- 古代 (kodai, “ancient times”)
- 五代 (Godai, “Five Dynasties”)
- 歳代 (-saidai, “decade”)
- 酒代 (sakudai, “alcohol expenses”)
- 月代 (sakuyaki), 月代 (tsumashiro, “shaved part of the forehead”)
- 三代 (sandai, “three generations”)
- 誌代 (shidai, “magazine's price”)
- 昭代 (shōdai, “glorious reign”)
- 初代 (shodai, “first generation”)
- 身代 (shindai, “fortune, property”)
- 次代 (jidai, “the next era”)
- 時代 (jidai, “period, epoch”)
- 重代 (jūdai, “successive generations”)
- 上代 (shōdai), 上代 (uwadai, “ancient times”)
- 城代 (shōdai, “chamberlain”)
- 聖代 (seidai, “magnificent imperial reign”)
- 盛代 (seidai, “prosperous era”)
- 世代 (sedai, “generation, the world”)
- 先代 (sendai, “family predecessor”)
- 舌代 (zetsudai), 舌代 (shitadai, “a notice”)
- 前代 (zendai, “previous generation”)
- 総代 (sōdai, “representative”)
- 大代 (daidai, “main telephone number”)
- 地代 (chidai), 地代 (jidai, “land rent”)
- 茶代 (chadai, “a tip”)
- 帳代 (chōdai, “curtained sleeping platform”)
- 手代 (tedai, “sales clerk”)
- 当代 (tōdai, “the present age”)
- 名代 (nadai, “well-known, fame”)
- 名代 (myōdai, “proxy, representative”)
- 苗代 (nawashiro), 苗代 (naeshiro, “rice nursery”)
- 年代 (nendai, “age, era”)
- 糊代 (norishiro, “overlap width”)
- 花代 (handai, “price of flowers”)
- 場代 (badai, “rent, cover charge”)
- 番代 (bandai, “taking turns”)
- 本代 (hondai, “money for books”)
- 間代 (madai, “room rent”)
- 末代 (matsudai, “forever, in perpetuity”)
- 御代 (miyo, “imperial reign”)
- 明代 (Mindai, “Ming dynasty”)
- 無代 (mudai, “free of charge”)
- 餅代 (mochidai, “money to see one over the New Year”)
- 宿代 (yadodai, “hotel charges”)
- 力代 (chikarashiro, “tax paid to avoid forced labor”)
- 依代, 依り代, 憑代 (yorishiro, “object representative of a divine spirit”)
- 累代 (ruidai, “successive generations”)
- 歴代 (rekidai, “successive generations”)
- 交代 (kōtai, “alternation, change”)
- 十代 (jūdai, “the teens”)
- 千代 (sendai), 千代 (chiyo, “thousand years”)
- 万代 (bandai), 万代 (mandai), 万代 (yorozuyo, “thousands of years”)
- 雪代 (yukishiro, “snow water”)
- 譜代 (fudai, “successive generations”)
- 田代芋, 田代薯 (tashiroimo, “taccad”)
- 何代目 (nandaime, “what ordinal number”)
- 親の代 (oya no dai, “parents' generation”)
- 食い代 (kuishiro, “food expenses”)
- 薬の代 (kusuri no shiro, “cost of medicine”)
- 削り代 (kezurishiro, “cutting stock”)
- 綴じ代 (dojishiro, “binding margin”)
- 取り代 (torishiro), 取代 (torishiro, “portion, one's share”)
- 縫い代 (nuishiro, “margin for a seam”)
- 飲み代, 飲代, 呑み代 (nomishiro, “drink money”)
- 君が代 (kimi ga yo, “imperial reign”)
- 締め代 (shimeshiro, “interference, jamming”)
- 身の代金, 身代金 (minoshirokin, “ransom”)
- バイト代 (baito-dai, “earnings from a part-time job”)
- 切符代 (kippudai, “ticket price”)
- 化粧代 (keshōdai, “lady's pin money”)
- 研削代 (kensakushiro, “grinding allowance”)
- 師範代 (shihandai, “assistant instructor”)
- 修理代 (jūridai, “cost of repairs”)
- 手術代 (shujutsudai, “surgery costs”)
- 食事代 (shokujidai, “cost of a meal”)
- 線香代 (senkōdai, “fee for a geisha's time”)
- 洗濯代 (sentakudai, “laundry charges”)
- 昼食代 (chūshokudai, “lunch price”)
- 治療代 (chiryōdai, “medical fees”)
- 電気代 (denkidai, “electric utility expense”)
- 暖簾代 (norendai, “goodwill”)
- 風呂代 (furodai, “fee charged at a public bath”)
- 部屋代 (heyadai, “room rent”)
- 弁当代 (bentōdai, “lunch money”)
- 御霊代 (mitamashiro, “symbol for the spirit of the dead”)
- 始生代 (Shiseidai, “Archean”)
- 原生代 (Genseidai, “Proterozoic”)
- 顕生代 (Kenseidai, “Phanerozoic”)
- 古生代 (Koseidai, “Paleozoic”)
- 中生代 (Chūseidai, “Mesozoic”)
- 新生代 (Shinseidai, “Cenozoic”)
- 大正の代 (Taishō no yo, “Taisho era”)
- 天神七代 (tenjin-shichidai, “seven generations of celestial deities”)
- 強直間代発作 (kyōchoku-kandai-hossa, “tonic-clonic seizure”)
- 千九百年代, 1900年代 (senkyūhyaku-nen dai, “the 1900s”)
- 明治天皇の代に (Meiji tennō no yo ni, “under Emperor Meiji's rule”)
Etymology 1
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 代 |
| しろ Grade: 3 |
| kun'yomi |
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]- (archaic) substitution
- (archaic) price, cost, charge
- (historical) shiro, a unit of land
Etymology 2
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 代 |
| よ Grade: 3 |
| kun'yomi |
| For pronunciation and definitions of 代 – see the following entry. | ||
| ||
| (This term, 代, is an alternative spelling of the above term.) |
Etymology 3
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 代 |
| だい Grade: 3 |
| on'yomi |
From Middle Chinese 代 (MC dojH).
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]- price
- generation of a family
- reign of a royal
- decade
- era
Counter
[edit]- generation of a royal family
- era, age, decade
Suffix
[edit]Alternative forms
[edit]- (period of time): 台
References
[edit]Korean
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Middle Chinese 代 (MC dojH).
- Recorded as Middle Korean ᄄᆡᆼ〮 (Yale: ttóy) in Dongguk Jeongun (東國正韻 / 동국정운), 1448.
- Recorded as Middle Korean ᄃᆡ〯 (tǒy) (Yale: tǒy) in Hunmong Jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527.
Pronunciation
[edit]- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [tɛ(ː)] ~ [te̞(ː)]
- Phonetic hangul: [대(ː)/데(ː)]
- Though still prescribed in Standard Korean, most speakers in both Koreas no longer distinguish vowel length.
Hanja
[edit]代 (eumhun 대신할 대 (daesinhal dae))
代 (eumhun 세대 대 (sedae dae))
- hanja form? of 대 (“to replace”) [prefix; affix]
- hanja form? of 대 (“generation”) [noun; suffix; affix]
Compounds
[edit]References
[edit]- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [2]
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]代: Hán Việt readings: đại (
代: Nôm readings: đời[1][2][3][4][5], đãi[1][2][3], đại[1][2][5], dạy[1][2], dậy[1][2], rượi[3][4], đười[1], đợi[1]
- chữ Hán form of đại (“representative”).
- chữ Nôm form of đời (“life; world; generation; era”).
Compounds
[edit]References
[edit]- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Enclosed CJK Letters and Months block
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Han phono-semantic compounds
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Sichuanese hanzi
- Dungan hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Taishanese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Sichuanese verbs
- Dungan verbs
- Cantonese verbs
- Taishanese verbs
- Gan verbs
- Hakka verbs
- Jin verbs
- Northern Min verbs
- Eastern Min verbs
- Hokkien verbs
- Teochew verbs
- Wu verbs
- Xiang verbs
- Middle Chinese verbs
- Old Chinese verbs
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Middle Chinese nouns
- Old Chinese nouns
- Chinese proper nouns
- Mandarin proper nouns
- Sichuanese proper nouns
- Dungan proper nouns
- Cantonese proper nouns
- Taishanese proper nouns
- Gan proper nouns
- Hakka proper nouns
- Jin proper nouns
- Northern Min proper nouns
- Eastern Min proper nouns
- Hokkien proper nouns
- Teochew proper nouns
- Wu proper nouns
- Xiang proper nouns
- Middle Chinese proper nouns
- Old Chinese proper nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 代
- zh:Geology
- zh:Grammar
- Chinese short forms
- Chinese terms with historical senses
- zh:Geography
- Chinese surnames
- Southern Min Chinese
- Beginning Mandarin
- Puxian Min lemmas
- Puxian Min hanzi
- Puxian Min verbs
- Puxian Min proper nouns
- Chinese simplified forms
- Elementary Mandarin
- Intermediate Mandarin
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese third grade kanji
- Japanese kyōiku kanji
- Japanese jōyō kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading だい
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading たい
- Japanese kanji with kun reading か・わる
- Japanese kanji with kun reading かわ・る
- Japanese kanji with kun reading かわ・り
- Japanese kanji with kun reading か・わり
- Japanese kanji with kun reading か・える
- Japanese kanji with kun reading よ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading しろ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading す
- Japanese terms spelled with 代 read as しろ
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms spelled with third grade kanji
- Japanese terms with 1 kanji
- Japanese terms spelled with 代
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- Japanese terms with archaic senses
- Japanese terms with historical senses
- Japanese terms spelled with 代 read as よ
- Japanese terms spelled with 代 read as だい
- Japanese terms read with on'yomi
- Japanese terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Japanese counters
- Japanese suffixes
- Japanese terms with usage examples
- ja:Units of measure
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Middle Korean hanja
- Korean terms with long vowels in the first syllable
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Nom












