舌
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Alternative forms
[edit]- In Traditional Chinese (Taiwan, Hong Kong and Macao), this character is written with 干 as the upper component, which is also the historical form found in the Kangxi dictionary.
- In Simplified Chinese, (mainland China and Singapore), Japanese Kanji, Korean Hanja and Vietnamese Nom script, this character is written with 千 as the upper component.
Han character
[edit]舌 (Kangxi radical 135, 舌+0, 6 strokes, cangjie input 竹十口 (HJR), four-corner 20604, composition ⿱千口(GJKV) or ⿱干口(HT))
- Kangxi radical #135, ⾆.
- Shuowen Jiezi radical №46
Derived characters
[edit]- Appendix:Chinese radical/舌
- 佸, 㓉, 咶, 姡, 𡯢, 恬, 括, 活, 狧, 𭥹, 栝, 𣭪, 𤈏, 䏦, 䄆, 𤫵, 甛, 䀨, 秳, 𥚇, 絬, 聒, 𬛥, 𦨯, 蛞, 話(话), 𧵳(䞌), 趏, 䟯, 𨈸, 𮝐, 䣶, 銛(铦), 𬺄, 𩈙, 颳, 餂, 𣽰, 䯏, 𬵏, 𪌩, 𧱳, 𪎾, 𪗽
- 刮, 㔚, 𢼤, 𣁳, 𣢯, 𤭇, 甜, 𬚸, 𫕛, 𫫞, 𮧺, 頢(𬱠), 𫬎, 鴰(鸹), 𭓯, 䒷, 筈, 髺, 䦚, 𡇜, 憩
- 适, 敌 (Simplified from the component 啇)
- 乱, 辞, 𦯠 (Simplified from the component 𤔔)
References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 1006, character 22
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 30277
- Dae Jaweon: page 1463, character 12
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 5, page 2941, character 1
- Unihan data for U+820C
Chinese
[edit]| trad. | 舌 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. # | 舌 | |
Glyph origin
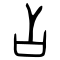
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 舌 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Shang | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
|

|

|
Pictogram (象形) – a forked tongue emerging upwards from a mouth (口). See also 言 and 音. Unrelated to 舍, in which it represents a hut.
Etymology 1
[edit]From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *s/m-l(j)a-t (“tongue”); compare Western Magar मेलेट (melet, “tongue”), Jingpho shinglet (“tongue”) (STEDT; Schuessler, 2009). The reconstruction of a complex initial *m(ə)-l- in Old Chinese is based on evidence from the softened initial in Proto-Min as well as Proto-Hmong-Mien *mblet (“tongue”) (Schuessler, 2007; Baxter and Sagart, 2014).
Alternatively, Schuessler (2007), reconstructing the Old Chinese minimally as *m-lat, derives it from 舐 (OC *m-leʔ, “to lick”) + *-t (“nominal suffix for natural objects”), literally “licker”.
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard)
- (Chengdu, Sichuanese Pinyin): se2
- Cantonese
- Gan (Wiktionary): set7
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): sah5
- Northern Min (KCR): ṳè
- Eastern Min (BUC): siĕk
- Southern Min
- Wu (Shanghai, Wugniu): 8zeq
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): she6
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄕㄜˊ
- Tongyong Pinyin: shé
- Wade–Giles: shê2
- Yale: shé
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: sher
- Palladius: шэ (šɛ)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʂɤ³⁵/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: se2
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: se
- Sinological IPA (key): /sɛ²¹/
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: sit3 / sit6
- Yale: sit / siht
- Cantonese Pinyin: sit8 / sit9
- Guangdong Romanization: xid3 / xid6
- Sinological IPA (key): /siːt̚³/, /siːt̚²/
- (Taishanese, Taicheng)
- Wiktionary: set5 / set4
- Sinological IPA (key): /set̚³²/, /set̚²¹/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: set7
- Sinological IPA (key): /sɛt̚²/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: sa̍t
- Hakka Romanization System: sad
- Hagfa Pinyim: sad6
- Sinological IPA: /sat̚⁵/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: sah5
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /saʔ⁵⁴/
- (Taiyuan)+
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: ṳè
- Sinological IPA (key): /yɛ⁴²/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: siĕk
- Sinological IPA (key): /sieʔ⁵/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
- chi̍h - vernacular;
- sia̍t - literary.
- Middle Chinese: zyet
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*mə.lat/
- (Zhengzhang): /*ɦbljed/
Definitions
[edit]舌
- (anatomy) tongue
- tongue-shaped object
- clapper of a bell
- (Hokkien, figurative) speech; speaking (used in certain expressions)
- a surname
Synonyms
[edit]Compounds
[edit]- 一番口舌
- 一簧兩舌 / 一簧两舌
- 七嘴八舌 (qīzuǐbāshé)
- 丁嘴鐵舌 / 丁嘴铁舌
- 三寸之舌
- 三寸舌
- 亂嚼舌頭 / 乱嚼舌头
- 伶口俐舌
- 佞舌
- 伸舌頭 / 伸舌头
- 使嘴使舌
- 兩舌 / 两舌
- 兩面二舌 / 两面二舌
- 刮舌子
- 劍舌槍脣 / 剑舌枪唇
- 動舌 / 动舌
- 半舌音
- 南蠻鴃舌 / 南蛮𫛞舌 (nánmánjuéshé)
- 卷舌 (juǎnshé)
- 反舌
- 反舌鳥 / 反舌鸟
- 口乾舌燥 / 口干舌燥 (kǒugānshézào)
- 口能舌便
- 口舌 (kǒushé)
- 口舌之便
- 口舌之快
- 口舌呆鈍 / 口舌呆钝
- 合嘴合舌
- 吐舌
- 吐舌頭 / 吐舌头
- 吞舌
- 告舌
- 咂嘴弄舌
- 咋舌 (zéshé)
- 咬舌
- 咬舌兒 / 咬舌儿 (yǎoshér)
- 咬舌子 (yǎoshézi)
- 咬舌根
- 咬舌頭 / 咬舌头
- 啖指咬舌
- 喉舌 (hóushé)
- 嘴嘴舌舌
- 嘴尖舌巧
- 嘴尖舌薄
- 嘵舌 / 哓舌
- 嘴舌
- 嚼舌 (jiáoshé)
- 嚼舌根
- 嚼舌頭 / 嚼舌头 (jiáo shétou)
- 墊舌根 / 垫舌根
- 壓枉造舌 / 压枉造舌
- 多嘴多舌
- 多嘴擦舌
- 多嘴饒舌 / 多嘴饶舌
- 大舌頭 / 大舌头 (dàshétou)
- 大費脣舌 / 大费唇舌
- 奴脣婢舌 / 奴唇婢舌
- 如簧之舌
- 婦人長舌 / 妇人长舌
- 婆子口舌
- 學舌 / 学舌 (xuéshé)
- 對嘴對舌 / 对嘴对舌
- 小舌 (xiǎoshé)
- 尖嘴薄舌
- 巧舌
- 巧言舌辯 / 巧言舌辩
- 帽舌 (màoshé)
- 廣長舌 / 广长舌
- 弄口鳴舌 / 弄口鸣舌
- 弄嘴弄舌
- 張儀舌 / 张仪舌
- 張口結舌 / 张口结舌 (zhāngkǒujiéshé)
- 張舌騙口 / 张舌骗口
- 徒廢脣舌 / 徒废唇舌
- 徒費脣舌 / 徒费唇舌
- 應嘴應舌 / 应嘴应舌
- 戳舌
- 拌嘴舌
- 拔舌地獄 / 拔舌地狱
- 拉舌頭 / 拉舌头
- 捏舌
- 捏舌頭 / 捏舌头
- 掉三寸舌
- 掉嘴弄舌
- 掉舌
- 捫舌 / 扪舌
- 捻舌
- 捲舌元音 / 卷舌元音
- 接舌子
- 捲舌音 / 卷舌音 (juǎnshéyīn)
- 捲舌韻母 / 卷舌韵母
- 掉舌鼓脣 / 掉舌鼓唇
- 提口拔舌
- 搬口弄舌
- 搖吻鼓舌 / 摇吻鼓舌
- 搬弄口舌
- 搬脣弄舌 / 搬唇弄舌
- 搬脣遞舌 / 搬唇递舌
- 搖脣鼓舌 / 摇唇鼓舌
- 搖舌 / 摇舌
- 搗謊駕舌 / 捣谎驾舌
- 撟舌 / 挢舌
- 攙話接舌 / 搀话接舌
- 木舌
- 杜口結舌 / 杜口结舌
- 杜口絕舌 / 杜口绝舌
- 枉口拔舌
- 枉費脣舌 / 枉费唇舌
- 柔舌
- 架舌頭 / 架舌头
- 油嘴滑舌 (yóuzuǐhuáshé)
- 泛脣泛舌 / 泛唇泛舌
- 浪舌
- 混嚼舌根
- 滿舌生花 / 满舌生花
- 火舌 (huǒshé)
- 為民喉舌 / 为民喉舌
- 煙生喉舌 / 烟生喉舌
- 爛了舌頭 / 烂了舌头
- 片口張舌 / 片口张舌
- 牛舌餅 / 牛舌饼
- 犁舌獄 / 犁舌狱
- 犯舌
- 甜嘴蜜舌
- 白話舌兒 / 白话舌儿
- 百舌 (bǎishé)
- 百舌之聲 / 百舌之声
- 百靈舌 / 百灵舌
- 目瞪舌僵
- 瞠目結舌 / 瞠目结舌 (chēngmùjiéshé)
- 碎嘴碎舌
- 磨舌頭 / 磨舌头
- 笨口拙舌 (bènkǒuzhuōshé)
- 筆舌 / 笔舌
- 箝口結舌 / 箝口结舌
- 糖舌蜜口
- 紅口白舌 / 红口白舌
- 結舌 / 结舌 (jiéshé)
- 結舌杜口 / 结舌杜口
- 緘口結舌 / 缄口结舌
- 緘舌閉口 / 缄舌闭口
- 美女破舌
- 翣舌
- 翻脣弄舌 / 翻唇弄舌
- 翹舌音 / 翘舌音
- 老婆舌頭 / 老婆舌头
- 能言舌辯 / 能言舌辩
- 脣槍舌劍 / 唇枪舌剑 (chúnqiāngshéjiàn)
- 脣槍舌戰 / 唇枪舌战
- 脣焦舌敝 / 唇焦舌敝
- 脣舌 / 唇舌
- 膏脣拭舌 / 膏唇拭舌
- 舌下神經 / 舌下神经 (shéxià shénjīng)
- 舌下腺 (shéxiàxiàn)
- 舌人 (shérén)
- 舌劍唇槍 / 舌剑唇枪 (shéjiànchúnqiāng)
- 舌劍脣槍 / 舌剑唇枪 (shéjiànchúnqiāng)
- 舌咽神經 / 舌咽神经 (shéyān shénjīng)
- 舌尖 (shéjiān)
- 舌尖元音
- 舌尖前音 (shéjiānqiányīn)
- 舌尖後音 / 舌尖后音
- 舌尖邊音 / 舌尖边音
- 舌尖音 (shéjiānyīn)
- 舌尖鼻音
- 舌弊耳聾 / 舌弊耳聋
- 舌戰 / 舌战 (shézhàn)
- 舌敝唇焦
- 舌敝脣焦 / 舌敝唇焦
- 舌本
- 舌根 (shégēn)
- 舌根音
- 舌根鼻音
- 舌炎 (shéyán)
- 舌狀花 / 舌状花
- 舌粲蓮花 / 舌粲莲花
- 舌耕 (shégēng)
- 舌苔 (shétāi)
- 舌葉 / 舌叶 (shéyè)
- 舌葉音 / 舌叶音 (shéyèyīn)
- 舌辯之士 / 舌辩之士
- 舌鋒 / 舌锋
- 舌門 / 舌门
- 舌面元音
- 舌面前音
- 舌面如鏡 / 舌面如镜
- 舌面後音 / 舌面后音
- 舌面音
- 舌音 (shéyīn)
- 舌頭 / 舌头 (shétou)
- 舌齒音 / 舌齿音
- 舔嘴咂舌
- 花嘴花舌
- 花舌 (huāshé)
- 花舌子
- 葉舌 / 叶舌
- 虛嘴掠舌 / 虚嘴掠舌
- 西施舌 (Xīshī shé)
- 觸舌 / 触舌 (tak-chi̍h) (Min Nan)
- 說舌 / 说舌
- 調嘴學舌 / 调嘴学舌
- 調嘴弄舌 / 调嘴弄舌
- 調嘴調舌 / 调嘴调舌
- 調脣弄舌 / 调唇弄舌
- 調舌弄脣 / 调舌弄唇
- 豁口截舌
- 貧嘴惡舌 / 贫嘴恶舌
- 貧嘴薄舌 / 贫嘴薄舌
- 貧嘴賤舌 / 贫嘴贱舌
- 貧嘴餓舌 / 贫嘴饿舌
- 費口舌 / 费口舌 (fèi kǒushé)
- 費盡脣舌 / 费尽唇舌
- 費脣舌 / 费唇舌
- 賣嘴料舌 / 卖嘴料舌
- 賣舌 / 卖舌
- 賣長舌 / 卖长舌
- 赤口毒舌
- 赤口白舌
- 赤舌燒城 / 赤舌烧城
- 軟嘴塌舌 / 软嘴塌舌
- 輕口薄舌 / 轻口薄舌
- 輕嘴薄舌 / 轻嘴薄舌
- 辯口利舌 / 辩口利舌
- 過舌 / 过舌
- 酒入舌出
- 重舌 (chóngshé)
- 金口木舌
- 金舌弊口
- 釘嘴鐵舌 / 钉嘴铁舌
- 鉗口吞舌 / 钳口吞舌
- 鉗口撟舌 / 钳口挢舌
- 鉗口結舌 / 钳口结舌
- 長舌 / 长舌 (chángshé)
- 長舌婦 / 长舌妇 (chángshéfù)
- 長舌頭 / 长舌头
- 閉口藏舌 / 闭口藏舌
- 雀舌
- 雞舌 / 鸡舌
- 雞舌香 / 鸡舌香
- 饒舌 / 饶舌 (ráoshé)
- 饒舌歌曲 / 饶舌歌曲
- 饒舌調脣 / 饶舌调唇
- 饕口饞舌 / 饕口馋舌
- 駟不及舌 / 驷不及舌
- 騙口張舌 / 骗口张舌
- 鬧口舌 / 闹口舌
- 鬧嘴舌 / 闹嘴舌
- 鴃舌 / 𫛞舌 (juéshé)
- 鴞心鸝舌 / 鸮心鹂舌
- 鴨舌帽 / 鸭舌帽 (yāshémào)
- 鴨舌草 / 鸭舌草
- 鸚鵡學舌 / 鹦鹉学舌 (yīngwǔxuéshé)
- 鹹嘴淡舌 / 咸嘴淡舌
- 鼓脣搖舌 / 鼓唇摇舌
- 鼓舌 (gǔshé)
- 鼓舌如簧 (gǔshérúhuáng)
- 鼓舌搖脣 / 鼓舌摇唇
- 齒亡舌存 / 齿亡舌存
- 齒弊舌存 / 齿弊舌存
- 齒舌 / 齿舌
- 齒落舌鈍 / 齿落舌钝
- 齰舌 / 𫜬舌
- 龍舌草 / 龙舌草
- 龍舌蘭 / 龙舌兰 (lóngshélán)
Descendants
[edit]- → Proto-Hmong-Mien: *mblet
Etymology 2
[edit]Glyph origin
[edit]| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 咶 | *qʰroːds, *qʰroːds, *ɡroːd |
| 話 | *ɡroːds |
| 刮 | *kroːd |
| 鴰 | *kroːd, *koːd |
| 趏 | *kroːd, *kʰroːd |
| 舌 | *ɡroːd, *ɦbljed |
| 姡 | *ɡroːd, *ɡoːd |
| 頢 | *ɡroːd, *koːd |
| 括 | *koːd |
| 活 | *koːd, *ɡoːd |
| 适 | *koːd, *kʰoːd |
| 栝 | *koːd, *l̥ʰeːmʔ |
| 佸 | *koːd, *ɡoːd |
| 髺 | *koːd |
| 聒 | *koːd |
| 銛 | *koːd, *slem, *l̥ʰeːmʔ |
| 葀 | *koːd |
| 懖 | *koːd |
| 筈 | *koːd, *kʰoːd |
| 萿 | *koːd |
| 蛞 | *kʰoːd |
| 闊 | *kʰoːd |
| 秳 | *ɡoːd |
Definitions
[edit]| For pronunciation and definitions of 舌 – see 𠯑 (“to block the mouth”). (This character is a variant form of 𠯑). |
References
[edit]- “舌”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[1], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Compounds
[edit]Etymology
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 舌 |
| した Grade: 6 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese, from Proto-Japonic *sita.
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ^ NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 [NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary] (in Japanese), Tokyo: NHK Publishing, Inc., →ISBN
Korean
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Middle Chinese 舌 (MC zyet).
Recorded as Middle Korean 쎠ᇙ〮 (Yale: ssyelq) in Dongguk Jeongun (東國正韻 / 동국정운), 1448.
Recorded as Middle Korean 설 (sel) (Yale: sel) in Hunmong Jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527.
Pronunciation
[edit]- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [sʰʌ̹ɭ]
- Phonetic hangul: [설]
Hanja
[edit]Compounds
[edit]References
[edit]- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [2]
Kunigami
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]舌 (shichā)
Miyako
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]舌 (suda)
Okinawan
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]舌 (shicha)
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]舌: Hán Nôm readings: thiệt, thịt, thĩa, thễ, sễ
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
Yaeyama
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]舌 (sïtā)
Yonaguni
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]舌 (tta)
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Shuowen radicals
- Han pictograms
- Chinese terms inherited from Proto-Sino-Tibetan
- Chinese terms derived from Proto-Sino-Tibetan
- Mandarin terms with audio pronunciation
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Sichuanese hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Taishanese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Middle Chinese nouns
- Old Chinese nouns
- Chinese proper nouns
- Mandarin proper nouns
- Sichuanese proper nouns
- Cantonese proper nouns
- Taishanese proper nouns
- Gan proper nouns
- Hakka proper nouns
- Jin proper nouns
- Northern Min proper nouns
- Eastern Min proper nouns
- Hokkien proper nouns
- Teochew proper nouns
- Wu proper nouns
- Xiang proper nouns
- Middle Chinese proper nouns
- Old Chinese proper nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 舌
- zh:Anatomy
- Hokkien Chinese
- Chinese surnames
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Middle Chinese verbs
- Old Chinese verbs
- Chinese variant forms
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese sixth grade kanji
- Japanese kyōiku kanji
- Japanese jōyō kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading ぜち
- Japanese kanji with goon reading ぜつ
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading せつ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading した
- Japanese terms spelled with 舌 read as した
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms inherited from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms derived from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms spelled with sixth grade kanji
- Japanese terms with 1 kanji
- Japanese terms spelled with 舌
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- ja:Anatomy
- ja:Organs
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Middle Korean hanja
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Kunigami kanji
- Kunigami sixth grade kanji
- Kunigami kyōiku kanji
- Kunigami jōyō kanji
- Kunigami kanji with kun reading しちゃー
- Kunigami terms with IPA pronunciation
- Kunigami lemmas
- Kunigami nouns
- Kunigami terms spelled with sixth grade kanji
- Kunigami terms with 1 kanji
- Kunigami terms spelled with 舌
- Kunigami single-kanji terms
- xug:Anatomy
- Miyako kanji
- Miyako sixth grade kanji
- Miyako kyōiku kanji
- Miyako jōyō kanji
- Miyako kanji with kun reading すだ
- Miyako terms with IPA pronunciation
- Miyako lemmas
- Miyako nouns
- Miyako terms spelled with sixth grade kanji
- Miyako terms with 1 kanji
- Miyako terms spelled with 舌
- Miyako single-kanji terms
- mvi:Anatomy
- Okinawan kanji
- Okinawan sixth grade kanji
- Okinawan kyōiku kanji
- Okinawan jōyō kanji
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading しちゃ
- Okinawan terms with IPA pronunciation
- Okinawan lemmas
- Okinawan nouns
- Okinawan terms spelled with sixth grade kanji
- Okinawan terms with 1 kanji
- Okinawan terms spelled with 舌
- Okinawan single-kanji terms
- ryu:Anatomy
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Yaeyama kanji
- Yaeyama sixth grade kanji
- Yaeyama kyōiku kanji
- Yaeyama jōyō kanji
- Yaeyama kanji with kun reading しぃたー
- Yaeyama terms with IPA pronunciation
- Yaeyama lemmas
- Yaeyama nouns
- Yaeyama terms with multiple readings
- Yaeyama terms spelled with sixth grade kanji
- Yaeyama terms with 1 kanji
- Yaeyama terms spelled with 舌
- Yaeyama single-kanji terms
- rys:Anatomy
- Yonaguni kanji
- Yonaguni sixth grade kanji
- Yonaguni kyōiku kanji
- Yonaguni jōyō kanji
- Yonaguni kanji with kun reading った
- Yonaguni terms with IPA pronunciation
- Yonaguni lemmas
- Yonaguni nouns
- Yonaguni terms spelled with sixth grade kanji
- Yonaguni terms with 1 kanji
- Yonaguni terms spelled with 舌
- Yonaguni single-kanji terms
- yoi:Anatomy
- CJKV radicals


