Wiktionary talk:About Dutch
Add topicGender
[edit]It would be nice if this page mentioned gender, and specifically whether it is correct to use "common" as a gender for Dutch words. -- Visviva 15:29, 1 March 2008 (UTC)
species ?
[edit]'This particular species of adverb'. English is not my native language, but I thought species refers to animals and plants, not adverb. My guess is, type is more appropriate here.
- It also commonly refers to molecules, ions, radicals in a chemical reaction Jcwf 17:10, 22 October 2008 (UTC)
IJ and ee.
[edit]You're right about most cases of verbs with 'ij' in it that become ones with 'ee' in the past tense, for example: strijken - streek - gestreken.
However, there is at least one verb with 'ij' that doesn't have this *probably because the 'ij' is at the beginning of the word*: ijken - ijkte - geijkt.
Just a thought. ;P
thoughts[c also 'translations',gr.pit]
[edit]- 'theSouth':ihatethat label>insted:brab,limb[whichcanbe aded!],e/w-fl,z-vl,etc
- how2ad say'paterkes,afmotten[=afslaan i/"standard"/macrolanguagedutch-flemish]' in wt?[brabantianISmy nativlanguage,n'NOTst.dutch which=4hollandRandstad!!
- the'taalunie'4/2me=DEAD.['n'i'lwork4that!!
- ihate "northern"condescendingnes i/general,n'itdoesnthelp wt i/particular!!
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dutch_dialects#Flanders
- sincerely--史凡/Sven - Pl also let me use voice-MSN/skype 2clarify as I suffer RSI and so cannot type very well! 07:56, 29 July 2009 (UTC)
- Translation: <<
- * "The South": I hate that label; what should be used instead: Brabantian, Limburgish (which can be added!), East/West Flemish,
Zeeuws-Vlaams/Zeelandian-Flemish, etc. - * How to add, say, paterkes [sic, diminutive (~tjes here) for monks], afmotten (which is afslaan in the standard macrolanguage Dutch-Flemish) in Wiktionary? Brabantian is my native language, and not Standard [i meant stupid,but fair enuf/enough ;) Dutch which is for Holland's Randstad!!
- * The TaalUnie for me is dead, and I will work to make sure of that!!
- * I hate "Northern" condescension in general, and it doesn't help Wiktionary in particular!!
- * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dutch_dialects#Flanders
- Sincerely, —Sven Please also let me use "voice-MSN/skype" to clarify as I suffer RSI and so cannot type very well/much! >> AugPi 01:03, 21 September 2009 (UTC)[+amendments,sv21.9.9]
- * "The South": I hate that label; what should be used instead: Brabantian, Limburgish (which can be added!), East/West Flemish,
- I created a template
{{Brabant}}and a category Category:Brabantian Dutch which I then used in the article afmotten. AugPi 01:31, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
- I created a template
- Limburgish and Dutch Low Saxon get to have their own L2 headers for articles, separate from Dutch. I guess that if the current test of Brabantian Wikipedia in the Incubator ever takes off (so that Brabantian succeeds in creating its own Wikipedia) then that would give you the green light to create Brabantian L2 headers, as if it were its own language, separate from Dutch. AugPi 02:01, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
- You have no obligation to use TaalUnie for Brabantian, since Brabantian is non-standardized (if I understand right). Of course, if Brabantian gets to be considered a separate language, then TaalUnie has nothing to do with Brabantian, and you are totally free from it! For my part, I work on Standard Dutch, so I find the/de TaalUnie useful, especially since I am non-native (and not quite fluent) in Dutch, i.e. the equivalent of a "retard" :) AugPi 02:24, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
noretrd,=mejust sensitiv w/this~mydisability,overeaction=myflaw tho:/
- ps myspanish not vgud;)--史凡>voice-MSN/skypeme!RSI>typin=hard! 08:12, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
- By the way, I sometimes add Dutch words which aren't listed by TaalUnie, for example: betegeling. I just made an educated guess that the word is feminine. AugPi 02:36, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
f+kosher,yup![im'api2help ,justshout!ta4ur nicereply:)[igot ignord be4+mistooku4a randstad dutch nativ speaker[sv 24.9.9]:/ ]--史凡>voice-MSN/skypeme!RSI>typin=hard! 08:12, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
- So the betegeling case proves that TaalUnie is not complete. On the other hand, I do assume that TaalUnie is sound, so that if a word is listed by TaalUnie, then that word exists "in real life". In other words, if a word is listed by TaalUnie, then it meets CFI. This can be useful for checking that given Dutch compound words are not just ad hoc compounds. AugPi 02:55, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
"inflected form of"
[edit]The entries speciale, actuele, achterwaartse, akoestische are all defined as "inflected form of...", without indicating what they're inflected for (which case or number or gender or...). The lemma-form entry also doesn't indicate. How is someone who comes across the word speciale in running text supposed to interpret it? (On the other hand, maybe the answer to this is very simple to anyone who knows even a little Dutch, which I do not.)—msh210℠ 23:02, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
- Basically, each Dutch adjective comes in two forms: (1) the lemma form, and (2) the inflected/alternate form. The use for the inflected form was explained here: http://en.wiktionary.org/w/index.php?title=Category:Dutch_adjective_forms&oldid=1993544 —AugPi 23:10, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
- So if the noun which follows the adjective is (1) masculine or feminine (or "common"), or (2) modified by a definite article: de or het, then the adjective should be "inflected" (i.e. suffixed with -e). —AugPi 23:13, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
- For purposes of translating to English, the lemma form and its "inflected" form are equivalent (i.e. translate to the same English word). —AugPi 23:17, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
- But this would be true of inflected adjectives in other languages as well, since English adjectives are not inflected. —AugPi 23:19, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
- But
Old EnglishMiddle English used to have adjectives inflected with -e ending, very similarly to modern Dutch. —AugPi 23:20, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
Quoted from a section on Medieval English in The Norton Anthology of English Literature. —AugPi 00:31, 14 August 2009 (UTC)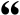
Adjectives ending in a consonant add final e when they stand before the noun they modify and after another modifying word such as the, this, that, or nouns or pronouns in the possessive: a good hors, but the (this, my, the kinges) goode hors. They also generally add e when standing before and modifying a plural noun, a noun in the vocative, or any proper noun: goode men, oh goode man, faire Venus.

- In Dutch, if an adjective is followed by a plural noun, then the adjective is "inflected" (i.e. is suffixed with -e) just like in Middle English. —AugPi 00:35, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- So a semantically plural adjective and a semantically definite adjective (except neuter) are inflected, if I understand you right. Perhaps instead of "inflected form of" it should say "plural or definite form of"?—msh210℠ 00:37, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- (1) A semantically plural adjective, (2) a semantically definite adjective (including neuter), or (3) a semantically masculine or feminine adjective, are inflected. —AugPi 02:18, 14 August 2009 (UTC) So it should be "plural or non-neuter or definite attributive form of".
- Anyway, see the article geel#Dutch: the word "inflected" in the inflection line now links to Appendix:Dutch_inflection#Adjectives and this seems IMHO a more satisfactory explanation than adding "plural or non-neuter or definite, attributive form of" in the inflection line, which would be cumbersome. —AugPi 13:04, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- Beautiful. Thanks.—msh210℠ 00:29, 17 August 2009 (UTC)
- Anyway, see the article geel#Dutch: the word "inflected" in the inflection line now links to Appendix:Dutch_inflection#Adjectives and this seems IMHO a more satisfactory explanation than adding "plural or non-neuter or definite, attributive form of" in the inflection line, which would be cumbersome. —AugPi 13:04, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- (1) A semantically plural adjective, (2) a semantically definite adjective (including neuter), or (3) a semantically masculine or feminine adjective, are inflected. —AugPi 02:18, 14 August 2009 (UTC) So it should be "plural or non-neuter or definite attributive form of".
- So a semantically plural adjective and a semantically definite adjective (except neuter) are inflected, if I understand you right. Perhaps instead of "inflected form of" it should say "plural or definite form of"?—msh210℠ 00:37, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- Possessive determiners also act like definite articles, since there are phrases such as
mijn goede boekmijn grote voorbeeld, mijn goede oor, and mijn goede doel whereboekvoorbeeld, oor, and doel are all neuter nouns. —AugPi 02:22, 14 August 2009 (UTC) - Also, demonstrative determiners appear to add definiteness, since there are phrases such as dit goede doel, dit kleine hart, and dit grote huis where doel, hart, and huis are all neuter. The phrases are not set phrases, just phrases I found on Google. —AugPi 02:44, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- In Dutch, if an adjective is followed by a plural noun, then the adjective is "inflected" (i.e. is suffixed with -e) just like in Middle English. —AugPi 00:35, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
isay [het]/zijn/dat grOOt vb.[maarmijntaal=VLOMS/ispeakbrabantian,andNOTdutch {which'dbe cald dutchFLEMISH4thepoliticalCONSTRUCT2work2SOM extent!ntheCOMNlang.'dbeENGLISH,buthatNOTwotheDUTCHexcel in,hapens w/INFLATED SELFESTEEM!![npl,givme somETHNIC'belgenmoppen/jokes aboutbelgianss,DISGUSTIN'ppl:(:(--史凡>voice-MSN/skypeme!RSI>typin=hard! 03:55, 14 August 2009 (UTC)
- Translation: I also say "[het] / zijn / dat groot voorbeeld", but my language is Flemish, I speak Brabantian, and not Dutch, the latter which should be called Dutch Flemish for the political construct to work to some extent! And the common language should be English, but that [is] not what the Dutch excel in, happens with inflated self-esteem!! And please, give me some ethnic belgenmoppen (=jokes about Belgians), disgusting!
people:( —Sven (voice-MSN/skype me! I have RSI which makes my typing hard!)" AugPi 00:31, 21 September 2009 (UTC)[+sv21.9.9]--史凡>voice-MSN/skypeme!RSI>typin=hard! 10:21, 21 September 2009 (UTC)
- If you not speak our language then please refrain from wanting to call the shots about it. You cannot have it both ways. Besides, your bigoted slurs are hardly acceptable in this environment. Jcwf 03:22, 23 September 2009 (UTC)
my nativ languag isnot "ur beautifl lang." indeed,tho ilikely no more boutit ,"ur lang",than u urslf,but as misleadin&st.coments r ur prerogative itseems,(i'v notisd 'em al overdaplace here,givin other editors (notjustme) ahardtime [w/ur pathetic1000edits here putin ofwilin ppl,thats wotrealy isnot needed here!!] cos of aledgd "messin'w/our (notmine,sure,hevn4bid,cant wait4da split st.dutch/flemish2ocur, alredy cos incompatibl ppl like u&me'lbe nicely separated2!) beautiful lang."[iheard serbian extremists state dasame crap 10+yrs ago] [sic],as if"dutch" alredy were alanguag,lemelaugh),amen.[me a bigot,of althenams ihear thats new--the racism i'd dadoutfl pleasure ofsufrin inwot,"je mooie (vrzuild vankanimeer)landje?" was v.real, jouw erfzonde,arogantpriksn u r.[aa-butnot livin their,ic,biblebelt must bewater2narowminded viskesgelekgij,tryin2turn datablz onme,shotscalr![iprovide myopinions&underlyin reasons,incl. pointin outcenturies-long foreign opresion i/flanders,which realy has2stop i/al its surreptitious forms,like continuin condescending betutteling from danorth,on wt&elsewhere,nhey,FTR im asmuch4the adition&inclusn ofsay veluws ,drents etc as re the1 of flemish langs/dialects asthey all need describd,but if,as4now,they mostlyneed2run under the "nl" hedr,u jcwf rda1 who'lneed2learn athing or2bout tolerance,insted of haughtily telin other ppl wot2do just cos in ur bigotd1trak-mind u prize urself of holdin'dalinguistic holy grail;praps4da randstad boutwhich idont care anymore sins my continuously so unsavory experiences overthere,darest ofda benelux is ling.more divers than useem2realiz,sincerely--史凡>voice-MSN/skypeme!RSI>typin=hard! 16:29, 23 September 2009 (UTC)
- You do not know much about me but have all your condescending prejudices and unfounded rants ready anyway. "I speak Brabantian, and not Dutch" you say? Then keep your hands off my language. Jcwf 18:52, 23 September 2009 (UTC)
Irregular verbs
[edit]{The following was cut/copied from the project page and pasted here:}
There are five verbs which are listed as "somewhat irregular" by Dutchgrammar.com, namely: gaan, slaan, staan, zien, and doen. These shall be (except for zien, vide infra) considered irregular by en.wiktionary, per insistence of CodeCat (talk • contribs), even if nl.wiktionary considers them strong. AugPi 01:57, 24 October 2009 (UTC)
The same, of course, goes for derivatives: afgaan, opgaan, etc.
Anyone who objects to this arrangement can feel free to set up or request for a vote.
- For doen, there is little to argue: it is irregular and categorized as such at nl.wikt. Staan en gaan are composits of staan/'standen' and gaan/'gangen' and one could certainly call them irregular for that reason. Slaan en zien are historically strong verbs but have developed some irregularity because a [h] sound either dropped out (sla[h]en, zi[h]en) or hardened to g: sloeh zah. I would consider them strong. It all depends on how much irregularity you wish to tolerate and how much you wish to reflect the historical development.
Jcwf 03:33, 24 October 2009 (UTC)
:Grunnen (talk • contribs) also considers zien to be strong. CodeCat sees the issue of regularity/irregularity through the eyes of a computer programmer which means that he is rather intolerant of irregularity for considering a verb to be strong (programming being a black & white kind of exercise). AugPi 04:05, 24 October 2009 (UTC)
If zien were considered strong then it would have to have a decent Etymology section.- See seon for that: it comes from *sehwan. Wiktionary is about language, not about algorithms I think. Jcwf 04:22, 24 October 2009 (UTC)
OK, it's Grunnen, Jcwf, and AugPi in favor of listing zien as strong, so it will be listed as strong.[struck out by AugPi 19:52, 27 March 2010 (UTC)]
- See seon for that: it comes from *sehwan. Wiktionary is about language, not about algorithms I think. Jcwf 04:22, 24 October 2009 (UTC)
- My reasons for treating zien as irregular is that it doesn't allow you to predict its forms using commonly established rules for Dutch grammar. It is an 'exception' to the rules. Imagine yourself as a language learner for a moment, someone who doesn't know all the forms of zien but does know how strong and weak verbs work. Given a form like 'zien', the first instinct would be to construct a stem zi- or zie-. The latter is correct as far as the present tense is concerned. But then, given the knowledge that it is a class 5 strong verb, one would expect the present tense to have -e- which changes to -a- in the past tense. So what do you do now? zia? za? The regular intuition of someone unfamiliar with the rules governing this specific verb break down. The forms of zien are unpredictable and do not match any other verb, so they can't be intuitively derived by someone who understands the rules. Marking the verb as irregular in the entry gives such a reader a clue that this verb does not conform to some common pattern, and therefore it might be wise to learn all the forms by heart rather than assuming that all forms can be derived from the infinitive alone. Also, aside from that, slaan shares the same irregularity as zien, so if zien is categorised as strong class 5, then slaan should go in strong class 6 for consistency. --CodeCat 12:00, 21 February 2010 (UTC)
- OK, zien and its derivatives are now marked as irregular. AugPi 18:22, 30 March 2010 (UTC)
Adverbs formed from adjectives
[edit]In Dutch, the predicative form of every adjective is automatically an adverb by form. This goes without saying and is an intrinsic part of Dutch grammar. I therefore propose that we do not list the adverb sense of an adjective if it is simply the same meaning (with -ly added) as the adjective. Any instances where this has been done already should be fixed to list only the adjectival meaning. Otherwise, [[Category:Dutch adjectives]] and [[Category:Dutch adverbs]] would contain pretty much the same entries, which is entirely redundant and not at all useful. —CodeCat 17:27, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- I disagree: en.wikt should be as NL-noob friendly as possible. Wikipedia is not paper, and the same is true of Wiktionary. A little apparent redundancy doesn't hurt. AugPi 17:29, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- meta:Wiki_is_not_paper
- ...Any instances where this has been done already should be fixed to list only the adjectival meaning. CodeCat...
- Many Dutch don't even distinguish grammatically between the two parts of speech. Learning about the difference is high school level, and takes considerable effort on the part of the students to understand. If the Dutch language itself and its speakers don't even make a distinction, why should Wiktionary? You shouldn't fit a language into a mold made for another language; the idea of duplicating entries of every adjective would seem quite absurd for any Dutch speaker. —CodeCat 17:37, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- ...Many Dutch don't even distinguish grammatically between the two parts of speech. CodeCat ...
- ...If the Dutch language itself and its speakers don't even make a distinction, why should Wiktionary? CodeCat ...
- en.wikt is written in English so it is primarily aimed for the use of English speakers, though users of other languages are also welcome. AugPi 17:45, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- And even if en.wikt were being used by a Dutch person, such use would probably only be for translating from Dutch to English, in which case that Dutch person would most definitely want to be made aware that there is a difference between English adjectives and adverbs. AugPi 17:51, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- English speakers are not generally familiar with the intricacies of Finnish grammar, yet we have no problem listing nähtäne as simply Impersonal potential present connegative form of nähdä. And that is just fine, because anyone who that entry would be of interest to, would know what that means. And what about an entry like cmavo? It doesn't even use a part of speech that any English speaker would understand! Yet I would think that we can reasonably expect someone who looks up a Lojban word to know what a gismu is. And in the same way, I think we can expect someone looking up a Dutch adverb to know that adjectives are adverbs in Dutch. —CodeCat 17:54, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- Yeah, and why not get rid of the FAQ link in the Chileense article? Surely we can assume that en.wikt readers looking up Dutch words will know what the "inflected form" is. Absolutely not, man! Please don't infuriate me! AugPi 18:24, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- Lojban is a butt-ugly pseudo-human computer language with how many speakers? —
- Answer: —
- Please don't compare Dutch with Lojban! 18:32, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
- Whoa, cool down a bit. If I can't present an argument without getting you all worked up, maybe you need a break or something? Seriously... O.O —CodeCat 18:35, 11 June 2010 (UTC)
Dutch vs. Flemish
[edit]Attention, Dutch speakers: Your opinions would be most welcome at [[Wiktionary:Beer parlour#"Redundant" languages]]. —RuakhTALK 13:11, 23 November 2010 (UTC)
Dutch attention is needed on this so far uncommented RFM proposal. Thanks —Μετάknowledgediscuss/deeds 04:41, 21 November 2012 (UTC)
Feasibility of automatic IPA
[edit]@Mnemosientje, Lingo Bingo Dingo, Alumnum, Morgengave I've made some automatic IPA generating modules in the past, and I've been wondering if making such a module for Dutch would be feasible. Dutch spelling-to-pronunciation rules are not as regular as for the other languages I've made modules for, so that makes it more of a challenge. The basic premise of the template, like many others like it, is that it tries to derive the IPA from the name of the page based on a set of rules. If the rules give the wrong result, then an adjusted "pronunciation respelling" is provided to the template.
I propose that the module assumes that stress is on the first syllable as a basic default. This seems like a relatively sensible assumption for many words. In theory it would be possible to refine this by writing additional rules to guess the stress with, but this only makes the operation of the module harder to understand, which then makes users less certain about when stress needs to be indicated explicitly. Perhaps if we limited it to words beginning with be-, ge-, her-, ont-, ver-, it would make some sense, but even then it would give incorrect results for words like beker, geler, herder, ontrouw and verder. I'm generally not a fan of defaults with exceptions, because then you tend to end up in situations where you have to do something special to make it go back to the original default, like here. Assuming stress on the first syllable is straightforward and everyone understands it.
Since stress is already indicated with an acute accent in some situations in Dutch, I propose to make this the default way to indicate stress to the template in the pronunciation respelling. On two-vowel combinations, the template should accept the accent on either both vowels (één) or just the first (éen), so that it's easier to put an accent on ij. Dutch orthography sometimes uses the vowel é as well, are there ever any cases where é is not stressed? If so, then these cases would need a pronunciation respelling.
The rules for detecting schwa can be relatively simple as a default too. Any single e in an unstressed syllable is considered a schwa, in a stressed syllable it follows the regular vowel length rules. A single e followed by a double consonant is always /ɛ/. An unstressed /ɛ/ would be indicated by the letter è, which is already used in some real words. è in an open syllable would indicate /ɛː/. —Rua (mew) 19:58, 18 December 2017 (UTC)
Re-examined
[edit]@Rua, Lambiam, Lingo Bingo Dingo (please ping any other editors if need be) I have created a test-version of an automatic IPA module on Module:User:Thadh/nl-IPA with a bunch of testcases at User:Thadh/sandbox. Do you have any feedback? I'm still working on making the phonetic IPA collapsable (as many different phonetic pronunciations could be given) and making it optional (similar reason, not all phonemic variants are found in all regions), but otherwise I'm eager to hear your thoughts, and also in the long run whether you think this would be helpful. Thadh (talk) 13:26, 30 October 2023 (UTC)
hottenˌtottenˌtententenˌtoonˌstellingis not a sentence andtententenis not even a word.Hottentotten(deprecated),tentenandtentoonstellingare words, which may be compounded (only in mentions) to the “fun word”hottentottententententoonstelling.- In our IPAizations of Dutch pronounciations, we indicate the optional /n/ of -en endings by using /...ə(n)/, which also applies word-internally: pannenkoek → /ˈpɑnə(n)ˌkuk/.
- Some words have an anomalous pronunciation, for example bijzonder → /biˈzɔn.dər/ instead of the expected spelling pronunciation */bɛi̯ˈzɔn.dər/. Some homographs have different senses with different syllable structures, e.g. valkuil is val + kuil or valk + uil. And homographs have different senses with different pronunciations, e.g.,
- And some words have several pronunciations. Therefore it should always be possible to override any defaults. Given the fact that an algorithmically produced pronunciation cannot be trusted but will always need to be checked, I feel it is best to aim for a set of rules that also tries its best to guess the stressed syllable.
- The algorithm can be tested against the existing entries in Category:Dutch terms with IPA pronunciation.
- --Lambiam 15:15, 30 October 2023 (UTC)
- @Lambiam:
- On no. 1, that's just me putting it under "sentences" on the page, it just tests stress. I do know Dutch grammar ;) The
ˌyou're seeing is not a word separation mark, it's a secondary stress; these have to be added manually. - I'm not sure the //ən// invalid IPA characters (//) -> [ə(n)] rule is true for all dialects, which is why I have decided not to add it to the phonemic pronunciation (but it is included in the phonetic one). If it is, I can easily add it to the phonemic transcription, too.
- Anomalous words are respelled, as done on the template. For instance, bijzonder would be respelled
{{nl-IPA|biˈzonder}}. Stress is defaulted to the first syllable. Similarly, syllable separaters can be added manually. The point of the module is not to make the phonetics much easier (although imo it does, slightly), but to allow for automatic addition of phonetic pronunciations.
- On no. 1, that's just me putting it under "sentences" on the page, it just tests stress. I do know Dutch grammar ;) The
- Hope this answers your questions :) Thadh (talk) 16:06, 30 October 2023 (UTC)
- With the /ən/ → [ə(n)] invalid IPA characters (//→[]) rule we have a perverse situation. In areas where pannen is pronounced as /ˈpɑnn̩/, Dutch pannekoek (from Middle Dutch panne + coeke) was pronounced /ˈpɑnəˌkuk/. Were the speakers there in 1996 supposed to not only change the orthography, but also their pronunciation? --Lambiam 17:41, 30 October 2023 (UTC)
- No, it was not supposed to effect a pronunciation change, although that it would introduce a change in spelling pronunciations was almost inevitable.
←₰-→Lingo Bingo Dingo (talk) 21:37, 30 October 2023 (UTC)
- No, it was not supposed to effect a pronunciation change, although that it would introduce a change in spelling pronunciations was almost inevitable.
- With the /ən/ → [ə(n)] invalid IPA characters (//→[]) rule we have a perverse situation. In areas where pannen is pronounced as /ˈpɑnn̩/, Dutch pannekoek (from Middle Dutch panne + coeke) was pronounced /ˈpɑnəˌkuk/. Were the speakers there in 1996 supposed to not only change the orthography, but also their pronunciation? --Lambiam 17:41, 30 October 2023 (UTC)
- @Lambiam:
==Inflection== -> ==Conjugation== and ==Declension==
[edit](Notifying Mnemosientje, Lingo Bingo Dingo, Azertus, Alexis Jazz, DrJos, Stujul): @Lambiam, Thadh Pinging people who were involved in recent Dutch discussions. Most languages use the headers "==Conjugation==" for verbs and "==Declension==" for nouns and adjectives. Dutch appears to use ==Inflection== though. I am planning to do a bot run to make the appropriate replacements and would like to get consensus for this. Benwing2 (talk) 09:53, 17 September 2024 (UTC)
- Agreed. I have been changing this already on Dutch entries wherever I see it, as I reckon that the headers Conjugation and Declension are more precise (I view it a bit like replacing
{{der}}with more precise templates like{{bor}}and{{inh}}). I note that not a small number of languages I commonly edit use solely or mostly the Inflection header, though, such as PGmc and PWGmc (where I have not made any changes away from Inflection), so I am not sure if there really is much of a wikiwide consensus. — Mnemosientje (t · c) 09:59, 17 September 2024 (UTC) - Agreed. I have been using these headers since I saw Mnemosientje using them, and was actually already considering making a bot request for this.
- Stujul (talk) 11:09, 17 September 2024 (UTC)
- I have also been changing these whenever I am editing Dutch entries, which to be honest isn't a lot. But yes, agreed, 100%. Thadh (talk) 16:47, 17 September 2024 (UTC)
- Fine with me. I’m generally in favour of consistency, as long as it is not a foolish one. --Lambiam 19:42, 17 September 2024 (UTC)
- This use of "Inflection" over the common alternatives was a Rua initiative of several years ago, which probably explains its existence in some older Germanic L2s as well (addressing @Mnemosientje's point). I am altogether indifferent as to which variant prevails.
←₰-→Lingo Bingo Dingo (talk) 06:42, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
one more ping on various topics
[edit](Notifying Mnemosientje, Lingo Bingo Dingo, Azertus, Alexis Jazz, DrJos, Stujul): @Lambiam, Thadh Sorry to ping everybody once again. Looking over the current state of Dutch lemmas and non-lemma forms, I am thinking of making the following changes and would like to make sure people are OK with them:
- Noun diminutives are currently treated as non-lemma forms. This seems contrary to the way it's done in other languages (e.g. German, Russian), and is done this way even when the meaning is unpredictable (instead of or in addition to a predictable diminutive). Examples of terms with unpredictable meanings are afspraakje "romantic date" (as well as the diminutive of afspraak); amsterdammertje "traffic bollard"; apenstaartje "at sign" (as well as the diminutive of apenstaart); beflapje "dental dam"; chocolaatje "piece of chocolate"; damespistooltje "small pistol"; draadschaartje "thread scissors"; etc. I'm thinking these should all be switched to be lemmas; or at the very least, we should do that for the terms with unpredictable meanings. Doing this for all lemmas would be a simple change to
{{nl-noun-dim}}; doing this only for the unpredictable meanings would entail splitting the POS entries in two, which isn't that much harder. - Adjective comparatives currently use the POS
adjective form. I'd like to switch them to usecomparative adjective, consistent with how other languages do things. Note thatcomparative adjectiveis still a non-lemma form; it's just a subcategory of adjective forms. Similarly, inflections of comparative adjectives (e.g. duchtigere, the inflected form of duchtiger) should probably usecomparative adjective forminstead ofadjective form, although I feel less strongly about this. - Creating shortcuts for common verb form inflections: Dutch currently has an adjective form shortcut
inflfor the "inflected form" (in -e) of an adjective, which is defined as follows:shortcuts["infl"] = {"m//f", "s", "attr", ";", "def", "n", "s", "attr", ";", "p", "attr"}This lets you write{{infl of|nl|duchtig||infl}}and not worry about the correct way to specify the actual inflections, which are expanded automatically. There is similarly a verb form shortcut2-invdefined as follows:shortcuts["2-inv"] = {"inv", "2", "s", "pres", "ind"}However, when used, bare verb forms like duelleer still use{{infl of|nl|duelleren||1|s|pres|ind|;|2-inv|;|imp}}, which is awkward. I'd like to create some verb form shortcuts, e.g.bare-verbfor bare verb forms like duelleer, and maybet-verbfor forms like duelleert (shortcut for the equivalent of23|s|pres|ind|;|p|imp),de-verbfor forms like duelleerde,den-verbfor forms like duelleerden, etc. These parallel existing English shortcuts likeed-form,ing-form,s-verb-form, etc. (see Module:form of/lang-data/en). - Running some hopefully noncontroversial cleanups on Dutch lemmas. These would include tasks 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 in Wiktionary:Grease_pit/2024/April#cleanup_run_on_Nordic_language_lemmas, which User:Thadh previously said were noncontroversial (not including #4, which moves synonyms/antonyms inline when safe to do so). Essentially, these are cleaning up raw links in Derived terms etc.; removing unnecessary uses of
{{l}}around English terms in definitions (since we now have JavaScript to do this automatically); templatizing raw category references; cleaning up Alternative forms sections to use{{alt}}; and standardizing the position of Wikipedia boxes.
Benwing2 (talk) 07:43, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
- I’m fine with all, inasmuch as I understand the ramifications – I rarely edit Dutch non-lemma forms, but I find many
{{infl of}}errors for Turkish entries, so getting it right is apparently hard for editors and well-chosen shortcuts are presumably welcome. - Using
comparative adjective formfor the POS parameter of{{head}}for forms like grotere is consistent with German entries; for example, schönere has{{head|de|comparative adjective form}}--Lambiam 09:05, 18 September 2024 (UTC)- Maybe the ideal solution is what's done for Portuguese (
{{pt-verb form of}}) and especially Arabic ({{ar-verb form}}).{{ar-verb form}}just needs to be told the lemma and conjugation type, looks up the appropriate conjugation definition(s) on the lemma page, finds which form(s) match the non-lemma page that invoked{{ar-verb form}}, and displays the correct{{infl of}}call automatically. This might be overkill for Dutch verbs, though, as they are much simpler than Portuguese or Arabic verbs, and shortcuts like the ones I'm proposing will probably work totally fine. Benwing2 (talk) 09:10, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
- I think in general diminutives should be treated as non-lemma forms, as they exist for basically any noun, and are derived very predictably. I agree that diminutive nouns with unpredictable meanings should be treated as lemmas.
- No opinion.
- Generally agree, although the situation is not as straightforward as in English. Which verb forms overlap is dependent on the ending of the stem, and whether the verb is strong or not (compare for example koken, wachten, komen). I would probably change the naming of
de-verbandden-verbtopast-sgandpast-plrespectively because of this. However, I believe most verbs would benefit from this. - Sure, though I would note for task 1 that Mnemosientje and I have been using
{{col-auto}}for Derived and Related terms. I would rather see the format changed to that instead.
- Maybe the ideal solution is what's done for Portuguese (
- Stujul (talk) 09:15, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
- @Stujul No objections to using
{{col-auto}}and thanks for your naming suggestions. Benwing2 (talk) 09:33, 18 September 2024 (UTC)- @Stujul I tabulated all the uses of
{{infl of}}and{{inflection of}}and tried to fill in descriptions and possible names. (There's a long tail of garbage, mostly needing cleanup, so I truncated at 50 uses.)
- @Stujul I tabulated all the uses of
- @Stujul No objections to using
| Description | Code | Uses | Expansion |
|---|---|---|---|
| plural past in -en, both strong and weak | past-pl |
3440 | p|past|ind|;|p|past|sub
|
| singular pres subj in -e, both strong and weak | leave as is? | 3281 | s|pres|sub
|
| present ending in -t | pres-t |
3113 | 23|s|pres|ind|;|p|imp
|
| bare form of verb (no ending) | bare-verb |
3097 | 1|s|pres|ind|;|2-inv|;|imp
|
| inflected adjective form; already a shortcut | leave as is | 2702 | infl
|
| singular past in -de/-te of weak verbs | past-sg |
2607 | s|past|ind|;|s|past|sub
|
| dependent-form plural past in -de/-te of separable-prefix weak verbs | dep-past-pl |
877 | p|dep|past|ind|;|p|dep|past|sub
|
| plural present in -en; only for separable-prefix verbs, because otherwise identical to infinitive | pres-pl |
876 | p|pres|ind|;|p|pres|sub
|
| singular past indicative of strong verbs | leave as is? | 817 | s|past|ind
|
| singular past subjunctive of strong verbs | leave as is? | 800 | s|past|sub
|
| dependent-form singular present subjunctive of separable-prefix verbs | leave as is? | 800 | s|dep|pres|sub
|
| dependent-form present ending in -t of separable-prefix verbs | dep-pres-t |
785 | 23|s|dep|pres|ind
|
| dependent-form bare form of verb (no ending) of separable-prefix verbs | dep-bare-form |
747 | 1|s|dep|pres|ind
|
| gij-form singular past indicative of strong verbs | leave as is? | 668 | 2-gij|s|past|ind
|
| partitive of adjectives | leave as is | 581 | par
|
| dependent-form singular past in -de/-te of weak separable-prefix verbs | dep-past-sg |
468 | s|dep|past|ind|;|s|dep|past|sub
|
| dependent-form singular past indicative of strong separable-prefix verbs | leave as is | 412 | s|dep|past|ind
|
| dependent-form singular past subjunctive of strong separable-prefix verbs | leave as is | 405 | s|dep|past|sub
|
| dependent-form gij-form singular past indicative of strong separable-prefix verbs | leave as is | 344 | 2-gij|s|dep|past|ind
|
| bare form of -ten verb (no ending) | bare-ten-verb |
337 | 123|s|pres|ind|;|imp
|
| bare form of verb with vowel stem or silent -e | maybe bare-verb|;|s|pres|sub |
98 | 1|s|pres|ind|;|2-inv|;|s|pres|sub|;|imp
|
| dependent-form bare form of -ten separable-prefix verb (no ending) | dep-bare-ten-verb |
98 | 123|s|dep|pres|ind
|
| not sure about this, maybe needs cleanup | ? | 76 | indef|m|and|f|s|;|indef|p|;|def
|
| not sure about this, maybe needs cleanup | ? | 66 | s|past|ind|;|s|past//pres|sub
|
| dependent-form bare form of verb with vowel stem | ? | 59 | 1|s|dep|pres|ind|;|s|dep|pres|sub
|
- @Stujul Forgot to sign. Benwing2 (talk) 07:30, 19 September 2024 (UTC)
- I think this looks good. Only,
dep-bare-formis inconsistent withbare-verb. That said,bare-verbis itself not consistent with the other forms, but I can't really think of a better name. - Stujul (talk) 12:22, 19 September 2024 (UTC)
- @Stujul Oops, I meant
dep-bare-verb. Thanks for catching it. Benwing2 (talk) 19:03, 19 September 2024 (UTC)
- @Stujul Oops, I meant
- I think this looks good. Only,
- @Stujul Forgot to sign. Benwing2 (talk) 07:30, 19 September 2024 (UTC)

